Snapshot
- A 15-year-old high school student presents with sudden weight loss, increased urination and increased thirst. He is an otherwise healthy individual who plays soccer on his schools team. On physical exam you see a lean young man with dry mucous membranes. Fingerstick glucose reveals a blood glucose of 469 mg/dL.
Insulin Overview
- Synthesis/Release
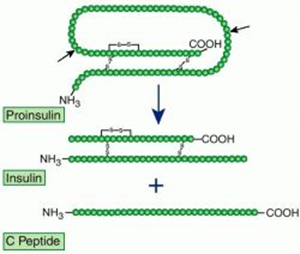
- synthesized as proinsulin in β cells of pancreas
- proinsulin = insulin + C-peptide
- hyperglycemia, GH, and cortisol ↑ insulin while hypoglycemia and somatostatin ↓ insulin secretion
- synthesized as proinsulin in β cells of pancreas
- Function
- ↓ glucagon release by α cells of pancreas
- ↑ Na+ retention (kidneys)
- ↑ glycogen synthesis and storage
- ↑ protein synthesis (muscles)
- recall babies of diabetic mothers are macrosomic
- ↑ cellular uptake of K+
- recall used with glucose to treat hyperkalemia
- Pathology
- a patient with an insulinoma will secrete abnormally high levels of insulin as well as C-peptide and will not produce anti-insulin antibodies
- these patients will have severe hypoglycemia
Glucagon Overview
- Production
- secreted by the pancreas (alpha cells)
- major stimulus for secretion is hypoglycemia
- major inhibition of secretion is hyperglycemia
- also inhibited by insulin and somatostatin
- Function
- increase blood levels of other energy forms
- lipolysis
- ketone body production
- increase blood levels of other energy forms
- Pathology
- a glucogonoma is a tumor that secretes excess glucagon leading to hyperglycemia as well as the characteristic rash of necrolytic migratory erythema


