Snapshot
- A 68-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with complaints of weakness and fatigue over the past half year. His medical history is significant for poorly-controlled diabetes. His family history is notable for type II diabetes in both of his parents and colon cancer in his father and older brother. A fecal occult blood test is performed and is shown to be positive for blood in the stool. A peripheral blood smear shows the following.
Introduction
- Overview
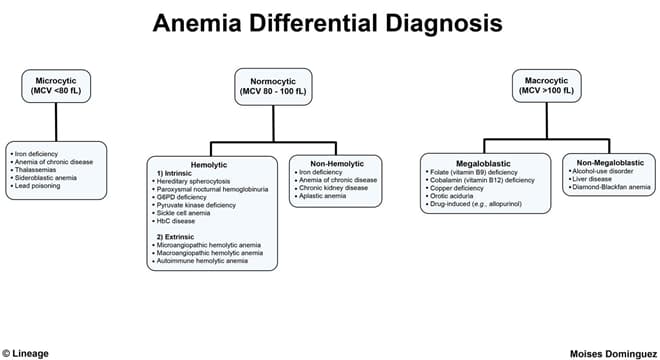
- iron deficiency anemia is a microcytic anemia that occurs when loss of iron exceeds intake
- may occur with insufficienty dietary intake of iron or in the setting of chronic blood loss
- treatment is usually with supplemental iron
- iron deficiency anemia is a microcytic anemia that occurs when loss of iron exceeds intake
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- most common anemia worldwide
- over 12% of the world’s population are affected
- demographics
- most commonly seen in adolescent girls and women of childbearing age
- due to blood loss from menstruation and childbirth
- most commonly seen in adolescent girls and women of childbearing age
- risk factors
- pregnancy
- menorrhagia
- occult bleeding (i.e., gastrointestinal blood loss)
- gastrointestinal parasites (i.e., hookworm), particularly in developing countries
- celiac disease
- incidence
- Pathophysiology
- gastrointestinal surgery
Presentation
- Symptoms
- fatigue
- weakness
- pica (craving for non-nutritious substances, such as ice, metal, hair, and paint)
- Physical exam
- conjunctival pallor
- tachycardia
- brittle nails
- restless leg syndrome
Studies
- Serum labs
- iron studies
- ↓ serum iron
- ↓ serum ferritin
- reflects low stores of iron in the body
- confirms the diagnosis of iron deficiency
- ↑ transferrin and total iron binding capacity (TIBC)
- complete blood count
- ↓ RBC count
- ↓ hemoglobin and hematocrit
- ↓ absolute reticulocyte count
- due to decreased production of RBCs
- iron studies
- Histology
- peripheral blood smear
- hypochromic and microcytic RBCs
- peripheral blood smear
- ↑ red cell distribution width (RDW)
Differential
- Thalassemia
- key distinguishing factors
- normal or ↑ RBC production
- normal or ↑ RBC count on CBC
- ↑ iron stores due to ineffective erythropoiesis and/or excessive blood transfusions
- key distinguishing factors
- Sideroblastic anemia
- key distinguishing factors
- presence of ringed sideroblasts on iron stain of a bone marrow aspirate
- key distinguishing factors
- ↑ iron stores
Treatment
- Lifestyle
- supplementation with replacement iron
- antacids may decrease iron absorption
- avoid cow’s milk before 12 months of age and limit intake in patients 1-5 years old
- supplementation with replacement iron


