Overview
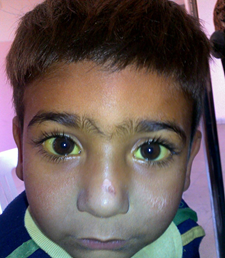
- Hyperbilirubinemia leading to yellowing of skin and eyes
- classified by ratio of conjugated bilirubin:total bilirubin
- CB < 20%
- Gilbert’s/Crigler Najjar syndromes
- physiologic jaundice of newborn
- hemolysis
- CB 20-50%
- viral hepititis
- CB > 50%
- drugs (e.g. OCP)
- Dubin-Johnson/Rotor syndromes
- primary biliary cirrhosis
- obstruction (e.g. stone)
- CB < 20%
- classified by ratio of conjugated bilirubin:total bilirubin
- Pathophysiology
- hepatocytes convert unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin into conjugated (direct) bilirubin
- performed by glucuronyl transferase enzyme to make bilirubin water soluble
- see Heme metabolism topic for normophysiology
- performed by glucuronyl transferase enzyme to make bilirubin water soluble
- bilirubin is not toxic at moderate levels
- high increases can result in kernicterus and death
- deposition of bilirubin in the brain
- hepatocytes convert unconjugated (indirect) bilirubin into conjugated (direct) bilirubin
- Types
- hemolytic
- destruction of RBCs than conjugation/excretion system can handle
- can result from
- hereditary hemolytic anemias, Rh incompatibility, ect.
- obstructive
- intrahepatic or bile duct block does not allow body to excrete bilirubin
- can result from
- oral contraceptives
- gallbladder stone
- carcinoma of the head of the pancreas
- hepatocellular
- damage to liver (i.e. hepatitis, cirrhosis) ↓ ability of conjugation/excretion system to handle normal bilirubin load
- hemolytic
| Jaundice Type | Hyper bilirubinemia | Urine Bilirubin | Urine Urobilinogen |
| Hepatocellular | Conjugated or unconjugated | ↑ | Normal/↓ |
| Obstructive | Conjugated | ↑ | ↓ |
| Hemolytic | Unconjugated | Absent | ↑ |


