Snap Shot
- A 15 year-old male does not demonstrate any signs of puberty. He is short for his age, his testicles show no evidence of enlargement, his testosterone levels are low, and he has a reduced ability to smell.
Introduction
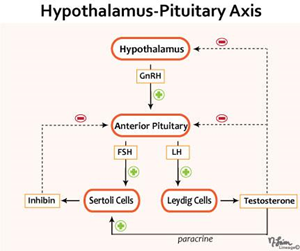
- Type of congenital hypogonadotropic hypogonadism with associated dysfunction of olfactory bulbs
- Associated with numerous genes (e.g., KAL1, KAL2, etc.)
- Failed migration of GnRH producing neurons from developping brain including passage to the cribiform plate
- Lack of GnRH results in
- ↓ LH, FSH, testosterone, sperm count
Presentation
- Cases can represent a range of symptoms and severity
- Non-reproductive features
- hypogonadotropic hypogonadism
- anosmia/hyponosmia
- cleft palate/craniofacial defect
- urogenital tract abnormalities
- syndactyly
- Reproductive features
- failure to start or fully complete puberty
- lack of testicle development
- primary amenorrhea
- poorly defined secondary sexual characteristics
- infertility
Treatment
- Hormone replacement
- exogenous estrogen in females
- exogenous testosterone in men
- Goals of therapy
- develop secondary sex characteristics
- build and sustain normal bone and muscle mass
- fertility


