Snapshot
- A 30-year-old man presents to the physician with his wife with concerns that they have been unable to get pregnant after trying for the past year. The patient’s wife has undergone a female infertility workup with no positive results. On physical examination, the man has scant hair in the axilla and pubic areas, small and firm testes, and the finding seen in the image. Karyotype testing is performed and reveals the presence of an extra X chromosome.
Overview
Introduction
- Overview
- Klinefelter syndrome is a sex chromosome disorder that is a common underlying cause of hypogonadism in men
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- 1 to 2.5 per 1000 men
- only 25-50% of Klinefelter syndrome patients are diagnosed during their lifetimes
- 1 to 2.5 per 1000 men
- risk factors
- advanced maternal age
- incidence
- Pathophysiology
- results in primary testicular failure with ↓ androgen production
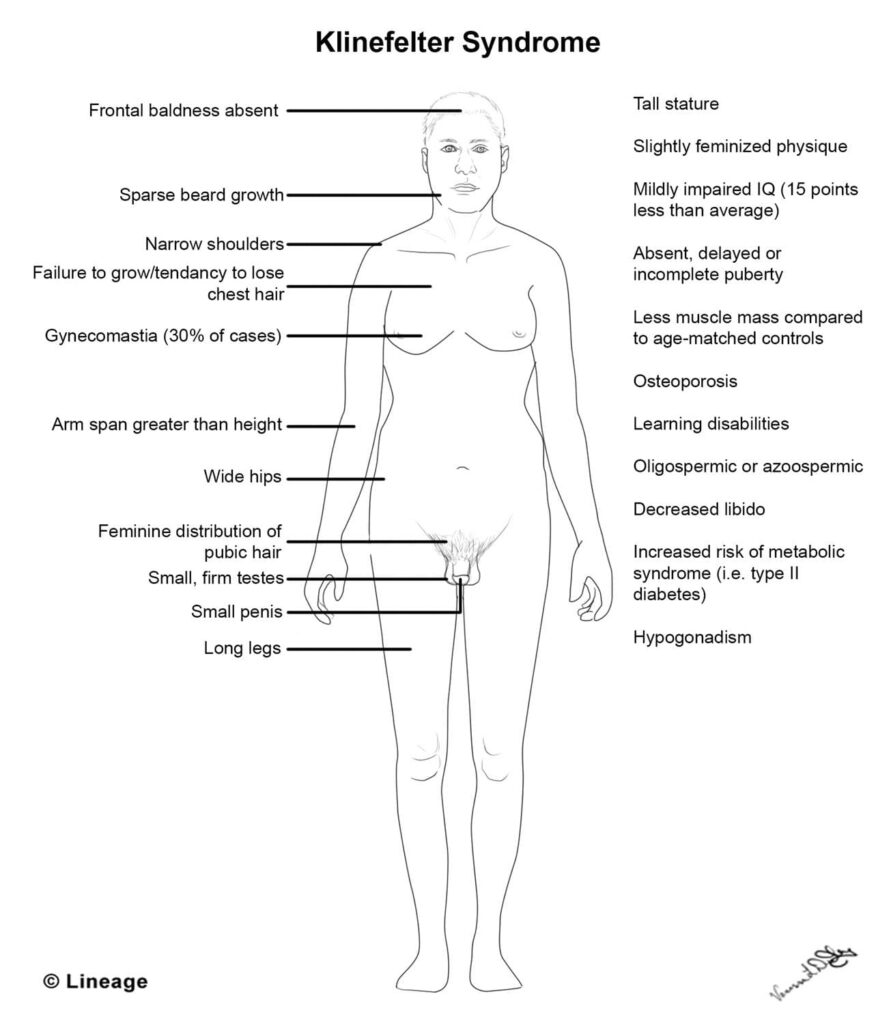
Presentation
- Symptoms
- infertility
- signs of androgen deficiency
- gynecomastia
- breast development at puberty
- sexual dysfunction
- osteoporosis
- gynecomastia
- Physical exam
- female hair distribution
- gynecomastia
- tall stature
- small, firm testes
Studies
- Karyotype
- karyotype 47,XXY provides a definitive diagnosis
- generally only recommended in prepubertal or pubertal boys, or men with clinical signs of Klinefelter syndrome who are seeking fertility treatment
- Serum hormone levels
- ↓ testosterone
- ↑ estradiol
- due to ↑ expression of aromatase
Differential
- Double Y males (47,XYY)
- key distinguishing factor
- phenotypically normal with intact fertility
- key distinguishing factor
- Fragile X syndrome
- key distinguishing factor
- enlarged testes
- key distinguishing factor
- Marfan syndrome
- key distinguishing factor
- intact fertility
Treatment
- Medical
- androgen (testosterone) replacement therapy
- indications
- promote development of normal male secondary sex characteristics
- indications
- androgen (testosterone) replacement therapy
- Lifestyle
- speech and behavioral therapy
- indications
- speech and behavioral therapy
- improve speech impairments and psychosocial problems
Complications
- ↑ risk of breast cancer
- incidence
- up to 50-fold ↑ incidence of male breast cancer compared to the normal population
- incidence


