Snapshot
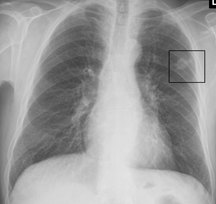
- A 40-year-old man presents with increasing muscle weakness. He reports difficulty rising from seated position and difficulty climbing stairs. He denies any blurry vision or any rashes on his body. He has a 100-pack-year history of smoking. Physical exam reveals proximal muscle weakness, decreased deep tendon reflexes, and dry mucous membranes. A bedside edrophonium test is conducted, which is negative. His chest radiography shows a suspicious finding – the round opacity shown in the square.
Introduction
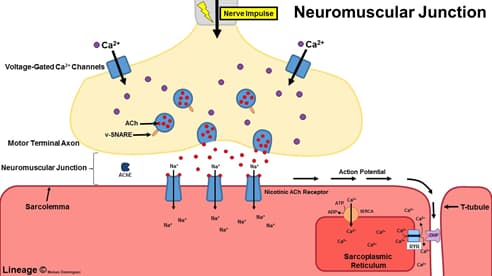
- Progressive weakness caused by autoantibody to presynaptic calcium channel on motor neurons
- type II hypersensitivity reaction
- Lambert-Eaton Syndrome (LES) also known as Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
- Epidemiology
- less common than myasthenia gravis
- Pathogenesis
- antibodies against presynaptic, voltage-gated Ca2+ channels at neuromuscular junction (see illustration)
- ↓ acetylcholine (ACh) release
- Associated conditions
- small cell (oat cell) carcinoma of lung
- recall other paraneoplastic secretions may be ACTH or ADH
- in 40% of patients with LES, cancer is found
- other autoimmune diseases
- small cell (oat cell) carcinoma of lung
- May be diagnosed with prolonged paralysis following use of neuromuscular blocking agents after surgery
Presentation
- Symptoms/physical exam
- proximal muscle weakness
- difficulty rising from a chair
- difficulty climbing stairs
- ↓ tendon reflexes
- autonomic symptoms
- dry mouth
- impotence
- improves temporarily with muscle use (vs myasthenia gravis, where symptoms worsen with muscle use)
- proximal muscle weakness
- spares extraocular muscles
Evaluation
- Negative edrophonium test
- cholinesterase inhibitor allows more ACh to present at the neuromuscular junction
- test is positive if patients regain strength
- test is negative in LES and positive in myasthenia gravis
- Voltage-gated Ca2+ channel antibody assay
- 75-100% of patients
- ACh receptor antibody assay
- more commonly positive in myasthenia gravis
- found occasionally in low titers in LES
Differential Diagnosis
Treatment
- Treat underlying malignancy
- Medical therapy for symptomatic treatment
- pyridostigmine inhibits acetylcholinesterase
- 3,4-diaminopyridine (DAP) increases the release of ACh
- Immunotherapy
- plasma exchange
- IVIG
- oral immunosuppressants azathioprine
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis
- if with simultaneous malignancy, prognosis is poorer
- LES does not affect respiratory system as significantly as myasthenia gravis does
- Complications
- impaired quality of life


