Overview
Introduction
- Leukocytes play an important role in eliminating offending agents
- neutrophils and macrophages are capable of destroying microbes, necrotic tissue, and foreign substances
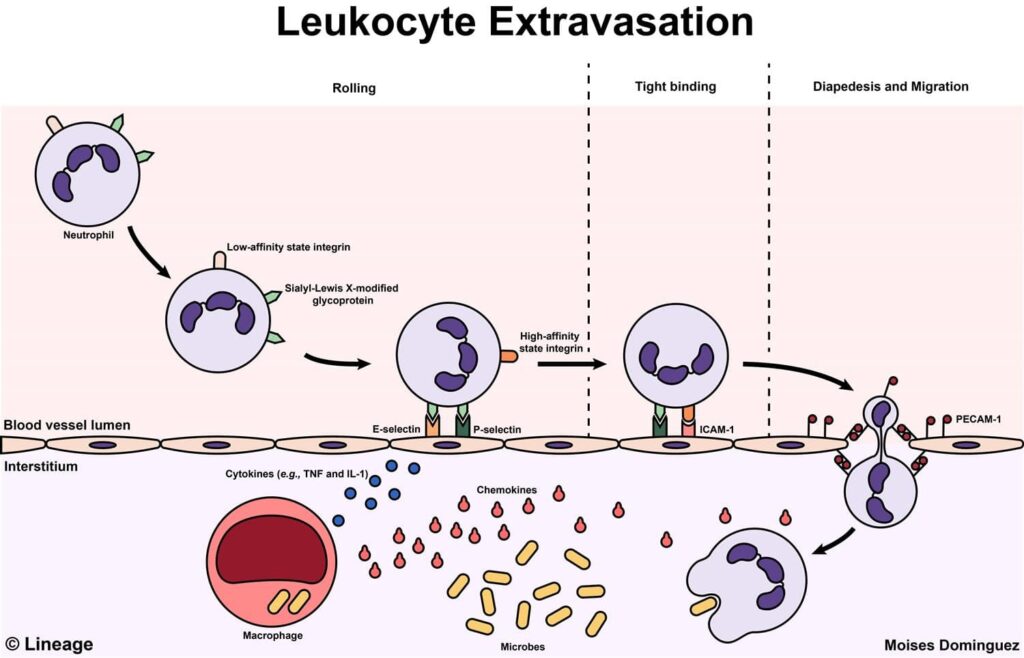
- The process of leukocytes migrating from the blood vessel to tissue involves multiple steps and are mediated by adhesion molecules and chemokines
- margination
- leukocytes become redistributed closer to the vessel wall
- rolling
- leukocytes transiently attach to endothelium and then detach
- these cells therefore “roll” on the vessel wall
- the endothelium possesses E-selectin and P-selectin
- cytokines from the inflamed tissue regulate selectin expression
- Sialyl-Lewis X protein binds to E-selectin and P-selectin
- found on leukocytes
- leukocytes transiently attach to endothelium and then detach
- firm endothelial adhesion
- mediated by integrin proteins
- vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 (VCAM1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) are found on the endothelium
- low affinity integrin are found on leukocytes
- mediated by integrin proteins
- migration through the vessel wall
- migration to tissue
- margination


