Overview
Snapshot
- A 72-year-old woman with a history of congestive heart failure, hypertension, and myocardial infarction presents with dyspnea on exertion and orthopnea. She does not have chest pain and denies any fever or chills. She does note increased swelling of her ankles but denies any other changes. Physical exam is notable for inspiratory crackles on lung ausculation and 2+ pitting edema on the bilateral lower extremities. Her physician increases the dose of one of her medications. One week later, she presents with muscle weakness and has an electrocardiogram that shows U waves. Serum electrolytes are drawn and her potassium level is found to be 2.8 mEq/L.
Furosemide
- Mechanism
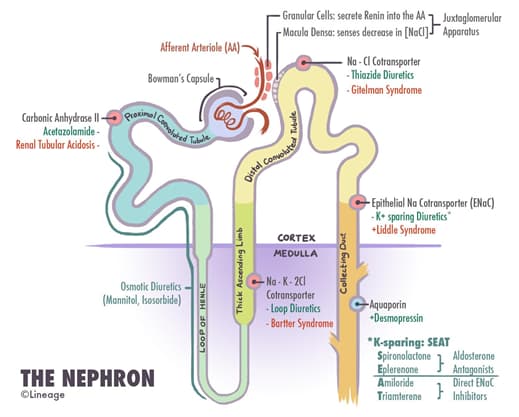
- blocks Na+/K+/2Cl- (NKCC) cotransport system in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle
- these electrolytes remain in the tubular lumen which
- prevents the formation of the medullary concentration gradient
- leads to less water reabsorption in the distal tubule
- blocking the NKCC cotransporter also prevents potassium back leaking into the lumen
- increased sodium delivery to the collecting duct leads to increased exchange with potassium and hydrogen
- these electrolytes remain in the tubular lumen which
- blocks Na+/K+/2Cl- (NKCC) cotransport system in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle
- Clinical use
- hypertension
- not first-line
- used in patients with concurrent hypertension and edema
- hypercalcemia
- anion overdose
- hypertension
- Toxicity
- electrolyte changes
- hypokalemia
- hypomagnesemia
- rarely, hypocalcemia
- contraction alkalosis
- hyperuricemia resulting in gout
- dehydration
- sulfa allergy
- interstitial nephritis
- enhanced toxicity with digoxin and lithium
- electrolyte changes
- Miscellaneous
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can decrease the response to loop diuretics due to decreased renal blood flow (RBF)
Ethacrynic acid
- Mechanism
- similar action to furosemide
- blocks NKCC cotransport system
- non-sulfa drug (phenoxyacetic acid derivative)
- similar action to furosemide
- Clinical use
- diuresis in patients allergic to sulfa drugs
- Toxicity
- more ototoxic than furosemide


