Overview
- Extent of Lungs
- base rests on the diaphragm
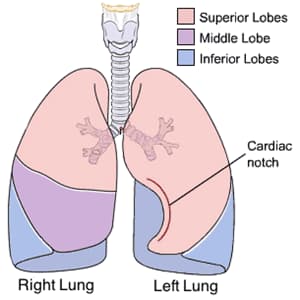
- Right Lung
- 3 lobes
- upper (superior), middle, and lower (inferior) lobes
- 2 fissures
- oblique (major) fissure separates upper and lower lobes
- horizontal (transverse) fissure separates upper and middle lobes
- 3 lobes
- Left Lung
- 2 lobes
- upper (superior) and lower (inferior) lobes
- 1 fissure
- oblique fissure
- cardiac notch
- an indentation consequent to the deviation of apex of heart to left side
- lingula is a flap of lung tissue of the left upper (superior) lobe that lies below cardiac notch
- homolog of right middle lobe
- lingula is a flap of lung tissue of the left upper (superior) lobe that lies below cardiac notch
- an indentation consequent to the deviation of apex of heart to left side
- 2 lobes
- Hilum of Lung
- a wedge-shaped area on mediastinal surface of each lung through which structures forming root of lung pass to enter or to exit lung
- Relationship of pulmonary artery (PA) to bronchus (“RALS”)
- right lung: anterior to bronchus
- left lung: superior to bronchus
- Trachea
- bifurcates into left and right (primary) main bronchi at level of sternal angle
- right (primary) main bronchus is shorter, wider, and runs more vertically
- bifurcates into left and right (primary) main bronchi at level of sternal angle


