Overview
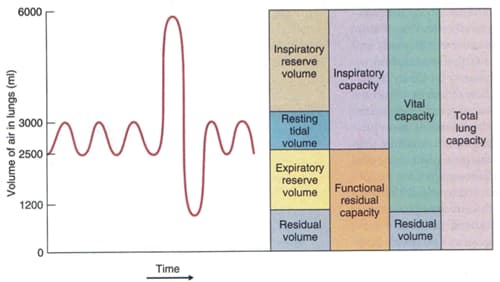
Lung Volumes
- Lung volumes are measured by spirometry
- Tidal Volume (TV)
- normal, quiet breathing involves inspiration and expiration of TV
- TV ~ 500 mL
- Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
- additional volume of gas that can be inspired above TV on maximal inspiration
- IRV ~ 3,000 mL
- Expiratory Reserve Volume (ERV)
- additional volume of gas that can be expired below TV on maximal expiration
- ERV ~ 1,200 mL
- Residual Volume (RV)
- volume of gas that remains in lungs following maximal expiration
- RV ~ 1,200 mL
- cannot be measured by spirometry
Lung Capacities
- a lung capacity includes ≥ 2 lung volumes
- Inspiratory Capacity (IC)
- TV + IRV
- IC ~ 3,500 mL
- Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
- ERV + RV
- volume of gas that remains in lungs following normal TV expiration
- equilibrium volume of lungs
- FRC ~ 2,400 mL
- Vital Capacity (VC)
- IC + ERV = TV + IRV + ERV
- volume of gas that can be expired following maximal inspiration
- VC ~ 4,700 mL
- Total Lung Capacity (TLC)
- VC + RV = TV + IRV + ERV + RV
- TLC ~ 5,900 mL
Pulmonary Vascular Resistance
- Lowest at FRC
- higher at volumes greater and less than FRC
- Contributions from both the intraalveolar vessels (bigger influence) and extraalveolar vessels
- Increased by
- inhalation
- increased pressure on intra-alveolar vessels by expanding alveoli
- forced exhalation
- increased intrathoracic pressure compresses pulmonary vessels
- inhalation



