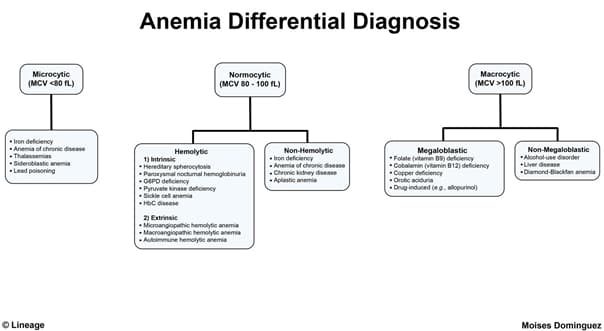
Introduction
- RBCs are damaged in systemic circulation due to force delivered in large caliber vessels or the heart itself
- Associated conditions
- calcified or stenotic heart valves
- most commonly aortic valve
Presentation
- Symptoms
- anemia
- fatigue
- jaundice
- pallor
- anemia
- shortness of breath
Evaluation
- Labs
- decreased Hgb
- increased reticulocyte %
- increased unconjugated bilirubin
- increased LDH
- decreased haptoglobin
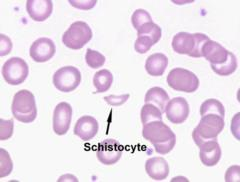
- Blood smear:
- schistocytes (helmet cells)
- due to shearing mechanical destruction
- burr cells (echinocytes)
- schistocytes (helmet cells)
- Normal platelet count
Treatment
- Pharmacologic
- chronic blood transfusions
- indicated for anemic episodes
- chronic blood transfusions
- Operative
- repair of defective valve OR replacement of previous prosthetic valve
- indicated in severe cases
- repair of defective valve OR replacement of previous prosthetic valve


