Snapshot
- A 30-year-old man with a marfanoid habitus presents for genetic counseling. His father, paternal uncle, and paternal great-grandfather died of sudden cardiac deaths. His father, specifically, suffered from an aortic dissection. As part of this patient’s work-up, he recently had cardiac imaging, which reveals a 5 cm aortic aneurysm. He is sent for further surgical consultation and is tested for suspected Marfan syndrome.
Overview
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- inherited connective tissue disorder characterized by aortic abnormalities and musculoskeletal deformities
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- clinical manifestations typically occur in adulthood
- demographics
- Pathogenesis
- fibrillins form a major part of connective tissues and provide structural support and elasticity to blood vessels, skin, and bones
- abnormalities in fibrillin can result in
- aortic abnormalities (cystic medial necrosis)
- ectopic lens (structural weakness in ligaments of the lens)
- skeletal deformities
- Genetics
- inheritance pattern
- autosomal dominant
- inheritance pattern
- Prognosis
- survival has improved with better management of aortic disease
- with early diagnosis and management, patients often have a normal life expectancy
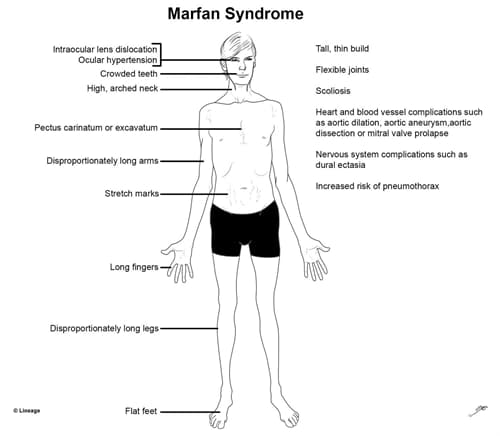
Presentation
- Physical exam
- skeletal
- tall and thin stature
- long extremities
- arm span exceeds height
- long fingers and toes (arachnodactyly)
- thumbnail protrudes beyond ulnar border of hand when crossed (thumb sign)
- thumb and little finger can encircle wrist (wrist sign)
- scoliosis
- hypermobile joints
- cardiovascular
- mitral valve prolapse
- mid-systolic click followed by a late systolic murmur
- aortic regurgitation
- diastolic murmur
- mitral regurgitation
- mitral valve prolapse
- skeletal
- high-pitched holosystolic murmur
Imaging
- Transthoracic echocardiography
- indication
- for all patients to evaluate for cardiac involvement
- findings
- mitral or aortic valve abnormalities
- indication
- aortic aneurysm or dissection
Studies
- Making the diagnosis
- based on clinical presentation
- genetic testing is not always necessary but is diagnostic
Differential
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- distinguishing factor
- hyperextensible skin and easy bruising
- distinguishing factor
- middle-sized artery aneurysms > aortic aneurysms
Treatment
- Management approach
- no curative treatment exists, so treatment is targeted at symptoms
- Conservative
- avoid high-impact contact sports
- indication
- for all patients
- indication
- avoid high-impact contact sports
- Medical
- β-blockers or angiotensin receptor blockers
- indications
- to halt the progression of aortic root dilation
- indications
- β-blockers or angiotensin receptor blockers
- Operative
- aortic aneurysm repair
- indication
- aortic aneurysm repair
- patients with aneurysms ≥ 4-4.5 cm
Complications
- Aortic dissection
- most common cause of death
- Congestive heart failure from cardiac valve abnormalities


