Snapshot
- A 7-year-old girl is brought to the pediatrician by her mother due to vaginal bleeding. The mother reports that her daughter appears happy, playful, and does exceptionally well in school. The mother says that she is in a healthy relationship with her husband, and the patient is an only child. The mother also states that the daughter reports pain “in her bones” and “stiffness.” On physical exam, the patient is conversational and not shy. There is tenderness to palpation of the lower extremities and a hyperpigmented spot with ragged edges on the left leg. Breast development is noted, and there is mild blood in the vaginal introitus without trauma to the external and internal vagina. The patient is referred to a pediatric endocrinologist.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- a rare genetic disorder characterized by
- polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
- café-au-lait spots
- endocrinopathy
- classically with precocious puberty
- others include hyperthyroidism, infantile Cushing syndrome, gigantism, and acromegaly
- a rare genetic disorder characterized by
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- precocious puberty is more common in females
- demographics
- early childhood
- incidence
- Pathogenesis
- Genetics
- inheritance pattern
- autosomal recessive
- inheritance pattern
- involved in G-protein signaling
Presentation
- Symptoms
- precocious puberty
- vaginal bleeding or breast development without pubic hair growth
- typically occurs at an earlier age than normal
- vaginal bleeding or breast development without pubic hair growth
- bone pain
- joint stiffness
- precocious puberty
- Physical exam
- pathologic fractures
- visible bone deformities may be found
Imaging
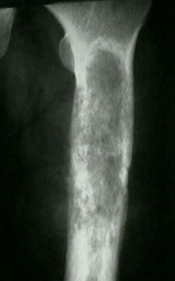
- Radiographs
- indication
- involved in the work-up of bone involvement (e.g., fracture)
- findings
- patchy areas of lytic bone lesions and sclerosis
- more commonly in the metaphyseal and diaphyseal regions
- patchy areas of lytic bone lesions and sclerosis
- indication
- trabeculated lesions with a ground-glass appearance may be found
Studies
- Labs
- molecular testing for GNAS1 analysis
Differential
- Neurofibromatosis type I
- has neurologic involvement and a family history of café-au-lait spots
Treatment
- There are no specific treatments for McCune-Albright syndrome
- treatment is aimed at the complications of this genetic disorder
Complications
- Increased risk for fracture



