Snapshot
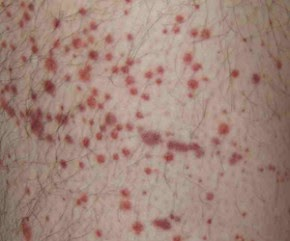
- A 19-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by his college roommate due to confusion and difficulty with arousing from sleep. The patient reports severe generalized headache, neck stiffness, and muscle aches. Temperature is 102.2°F (39°C), blood pressure is 102/68 mmHg, pulse is 107/min, and respirations are 22/min. On physical exam, a petechial rash is distributed on the thorax and extremities. While supine, neck flexion lead to involuntary knee flexion. (Meningococcal meningitis)
Introduction
- Inflammatory disease of the meninges
- Etiology (see the Microbiology of Meningitis topic )
- aseptic (viral)
- bacterial
- fungal
- non-infectious (e.g., systemic erythematosus lupus)
- drug-induced
Presentation
- Symptoms
- fever
- neck stiffness
- photophobia
- seizures
- Physical exam
- positive Kernig sign
- patient supine
- knee extension while hips are 90° flexed → resistance/pain
- positive Brudzinski sign
- patient supine
- passive neck flexion → involuntary knee flexion
- petechial rash
- positive Kernig sign
- may suggest Neisseria meningitidis infection
Evaluation
Lumbar puncture for CSF studies
| Cerebrospinal Fluid Analysis | ||||
| Test | Normal | Bacterial | Viral | Fungal/TB |
| Opening pressure | ≤ 20 cm H 2O | ↑ | Normal or slightly ↑ | ↑ |
| Color | Clear | Cloudy | Clear | Cloudy |
| Cell count | 0-5 cells/µL | ↑ (PMN) | ↑ (Lymphocytes) | ↑ (Lymphocytes) |
| Protein | < 45 mg/dL | ↑ | Slighty ↑ | ↑ |
| CSF:Serum glucose | > 0.6 | ↓ | Normal | ↓ |
- Blood tests
- blood cultures
- complete blood cell count
- C-reactive protein
Differential
- Lyme disease
- Neurosyphilis
- Drug-induced meningitis
- e.g., NSAIDs and amoxicillin
- Non-infectious mengitis
- e.g., systemic lupus erythematosus
- Stroke
Treatment
- Aseptic (viral) meningitis
- herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus
- acyclovir
- herpes simplex virus and varicella-zoster virus
- Bacterial meningitis
- when organism is unknown
- vancomycin
- ceftriaxone
- ampicillin
- add if > 50 years or immunocompromised
- add dexamethasone if suspected pneumococcal meningitis
- chemoprophylaxis for close contacts in meningococcal meningitis
- when organism is unknown
- e.g., rifampin, ceftriaxone, and ciprofloxacin
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Complications
- bacterial meningitis
- may lead to SIADH
- bacterial meningitis


