Overview
- Menopause
- signals end of menstrual cycles and reproductive function in females
- progressive loss of ovarian follicle units (atresia) throughout reproductive life causes a decrease in ovarian production of estrogen and reduces negative feedback to anterior pituitary, leading to an increase in FSH and LH levels
- typically preceded by several years of abnormal menstrual cycles
- e.g., anovulatory cycles
- in post-menopausal women, source of estrogen includes ovary and adrenal cortex
- via peripheral aromatization of androgens
- adrenal cortex (major) and ovary (minor) are sources of androstenedione
- ↑ androgens result in a male pattern hair growth (mainly on the face)
- adrenal cortex (major) and ovary (minor) are sources of androstenedione
- via peripheral aromatization of androgens
- average age of menopause is 50 years
- onset early in smokers
- early menopause may indicate premature ovarian failure
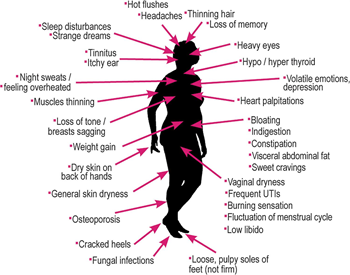
- Menopause symptoms
- symptoms are caused by loss of ovarian source of estrogen
- male-pattern hair growth in women via ↑ androgens
- hot flashes (vascular instability)
- atrophy of vagina (thinning of vaginal epithelium)
- ↓ vaginal secretions
- osteoporosis
- coronary artery disease
- symptoms are caused by loss of ovarian source of estrogen


