Introduction
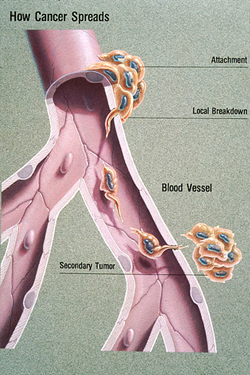
- Spread of a neoplasm to distant tissues
- Cellular requirements
- invasive carcinoma progression that reaches a blood or lymph vessel
- increased angiogenesis at metastatic foci
- ability to survive in distant tissue
- May spread hematogenously or via lymphatics
- sarcomas most commonly spread via blood
- carcinomas most commonly spread via lymphatics
- most notable exceptions include renal cell carcinomas, follicular carcinomas of the thyroid, and hepatocellular carcinoma
- all prefer hematogenous spread
- most notable exceptions include renal cell carcinomas, follicular carcinomas of the thyroid, and hepatocellular carcinoma
- If neoplasm is multifocal and well-circumscribed, strongly consider metastasis
- Most common sites of metastasis include
- lung
- liver
- metastasis much more common than primary tumors
- brain
- metastasis equivalent in frequency to primary tumors
- bone
- metastasis much more common than primary tumors
- lymph nodes are the most common site of metastasis
- These organs receive a large proportion of blood supply making metastatic seeding more likely in these areas
Metastasis to brain
- Due to blood flow patterns and masses normally present at gray-white border
- Primary tumors that metastasize to brain include
- lung > breast > skin (melanoma) > kidney (renal cell carcinoma) > GI
- pulmonary circulation immediately enters the brain once leaving left heart
Metastasis to liver
- The liver and lung are the most common sites of metastasis after the regional lymph nodes
- Primary tumors that metastasize to the liver include
- colon > stomach > pancreas > breast > lung
- colon drained by portal vein which empties into liver
Metastasis to bone
- Primary tumors that metastasize to the bone include
- prostate = breast > thyroid > testes > lung > kidney
- vertebrae seeded by Batson’s venous plexus
- Metastasis to bone may be bone forming (blastic) or bone destructive (lytic)
- prostate = blastic
- presents with high alkaline phosphatase
- breast = both lytic and blastic
- prostate = blastic


