Overview
- Airway lining
- simple ciliated columnar epithelium extends to the terminal bronchioles
- ciliated cuboidal cells extend to the respiratory bronchioles
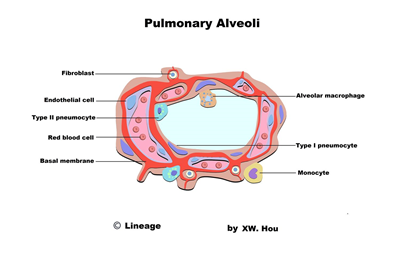
- alveolar sac are composed of pneumocytes
- macrophages clear debris in alveoli
- goblet cells extend to the larger bronchioles but stop before the terminal bronchioles
- Type I pneumocytes
- 97% of alveolar surfaces
- line the alveoli
- squamous
- thin for optimal gas diffusion
- Type II pneumocytes
- 3% of alveolar surfaces
- secrete pulmonary surfactant within lamellar bodies
- dipalmitoyl phosphatidylcholine
- lowers the alveolar surface tension
- serve as precursors to type I cells and other type II cells
- proliferate during lung damage
- Club (Clara) cells
- nonciliated
- columnar with secretory granules
- secrete component of surfactant
- degrade toxins
- act as reserve cells
- A lecithin-to-sphingomyelin ratio of > 2.0 in amniotic fluid is indicative of fetal lung maturity


