Introduction
- Multiple myeloma is cancer of monoclonal plasma cells
- produces large amounts of IgG (55%) or IgA (25%)
- high levels of IL-6 may be present
- Epidemiology
- most common primary tumor arising within bone in the elderly
- If asymptomatic
- called monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS)
- increased gamma globulin on serum electrophoresis but no symptoms of multiple myeloma are present
- Pathophysiology
- initial event – abnormal response of B lymphocyte to antigenic stimulation results in monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells -> MGUS
- additional mutations causes progression from MGUS to multiple myeloma
- since the plasma cell population in multiple myeloma are clones, they produce the same antibody, resulting in the monoclonal M spike on serum protein electrophoresis
- though total serum antibody levels increase, these antibodies do not provide protection against pathogens because there is a lack of antibody antigenic diversity
Presentation
Evaluation
- Serum protein electrophoresis
- monoclonal immunoglobulin spike (M protein)
- Urinalysis
- Peripheral blood smear
- RBC rouleaux formation
- Igs coat RBC and neutralize the ionic charge than normally repels RBCs
- RBC rouleaux formation
- Bone marrow aspiration
- Serology
- hypercalcemia
- result of bone degradation due to cytokine production that activates RANK receptor on osteoclasts
- associated with decreased phosphate, increased PTH-rp and decreased vitamin D levels
- prolonged bleeding time
- hypercalcemia
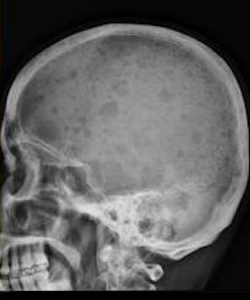
- Imaging
- punched-out lytic bone lesions on x-ray
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications


