Snapshot
- A 32-year-old women presents to her physician complaining of double vision. This has been very distressing for her. She has a past medical history significant for type 1 diabetes, treated with a continuous subcutaneous insulin pump. Upon further questioning, she mentions she experienced arm weakness and numbness that resolved spontaneously over the course of a couple weeks. Physical examination is notable for impaired adduction of the right eye, and nystagmus on abduction of the left eye on left lateral gaze.
Introduction
- Autoimmune inflammation/demyelination of CNS neurons
- specific anti-MBP (myelin basic protein) antibodies
- can find ↑ protein (IgG) in CSF
- over time white matter plaques accumulate in the brain and the spinal cord
- specific anti-MBP (myelin basic protein) antibodies
- Epidemiology
- gender bias
- ↑ in women
- race bias
- ↑ in whites
- onset commonly between 20-40 years
- ↑ in temperate climates
- gender bias
- associated with HLA-DR2
Presentation
- Symptoms – may have multiple neurologic symptoms separated in time and space
- motor involvement
- hemiparesis
- MLF syndrome → internuclear ophthalmoplegia
- nystagmus
- scanning speech (sound intoxicated)
- intention tremor
- sensory involvement
- hemisensory symptoms
- autonomic involvement
- motor involvement
- bladder/bowel incontinence
Evaluation
- LP
- ↑ leukocytes
- ↑ γ-globulins
- results in oligoclonal banding
- ↑ MBP
- normal glucose
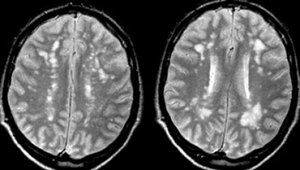
- Imaging
- must include two demyelinating lesions separated in time and space
- MRI is gold standard
- hyperintense on T2 and FLAIR with enhancement of acute lesions
- demyelinating periventricular plaques known as Dawson’s fingers
- may have preservation (early) or destruction (late) of axons within plaques
Differential
- Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
- Neuromyelitis optica (NMO)
- Idiopathic transverse myelitis
Treatment
- Medical
- β-interferon
- high-dose steroids (dexamethasone)
- speed recovery of ocular symptoms but do not change overall progression of disease
- glatiramer
- natalizumab
- ↑ risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- rituximab
- ↑ risk of progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy
- Symptomatic treatment for neurogenic bladder, spasticity, and pain
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Can exhibit multiple patterns of disability progression
- primary progressive – steady decline in function over time
- relapsing remitting – periods of relative stability alternating with declines
- secondary progressive – relatively stable at first followed by steady decline


