Overview
Snapshot
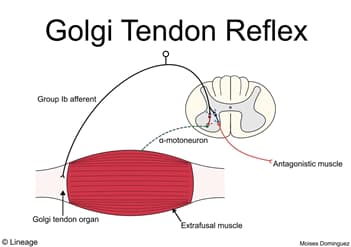
- A 67-year-old male is seen by his physician for a health-maintenance examination. He is currently doing well, but is distressed about poor muscle movement of his right arm. Approximately 6 months ago the patient was hospitalized for the management of an acute stroke. On physical examination, his right arm is hypertonic. When attempting to passively flex the arm, the physician noted resistance. Eventually, the joint rapidly closed. (Clasp-knife reflex – an exaggerated golgi-tendon reflex)
Introduction
- Skeletal muscle contraction and relaxation plays an important role in maintaining posture and movement
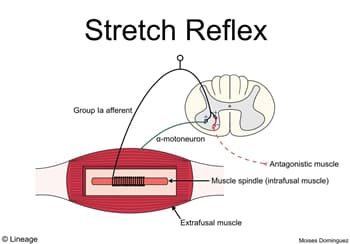
- Motor unit = single motor neuron + muscle fibers
- motor neuron can innervate few to many muscle fibers
- Two types of motor neurons:
- α-motoneurons
- innervates extrafusal muscle fibers (fibers that cause contraction)
- γ-motoneurons
- innervates intrafusal muscle fibers, a component of the muscle spindle
- adjusts muscle spindle sensitivity
- α-motoneurons and γ-motoneurons co-activation
- ensures the muscle spindle remains sensitive to changes in muscle length (eg, contraction)
- α-motoneurons


