Overview
- Exogenous cell injury resulting in uncontrolled cell degradation
- normal cellular enzymes responsible for controlled cell death (apoptosis) are inactivated
- Key principles
- release of intracellular components
- presence of inflammation
- Several types
- coagulative
- solid organs which allow preservation of cell shape by coagulation of cell proteins
- e.g.) heart, liver, kidney
- solid organs which allow preservation of cell shape by coagulation of cell proteins
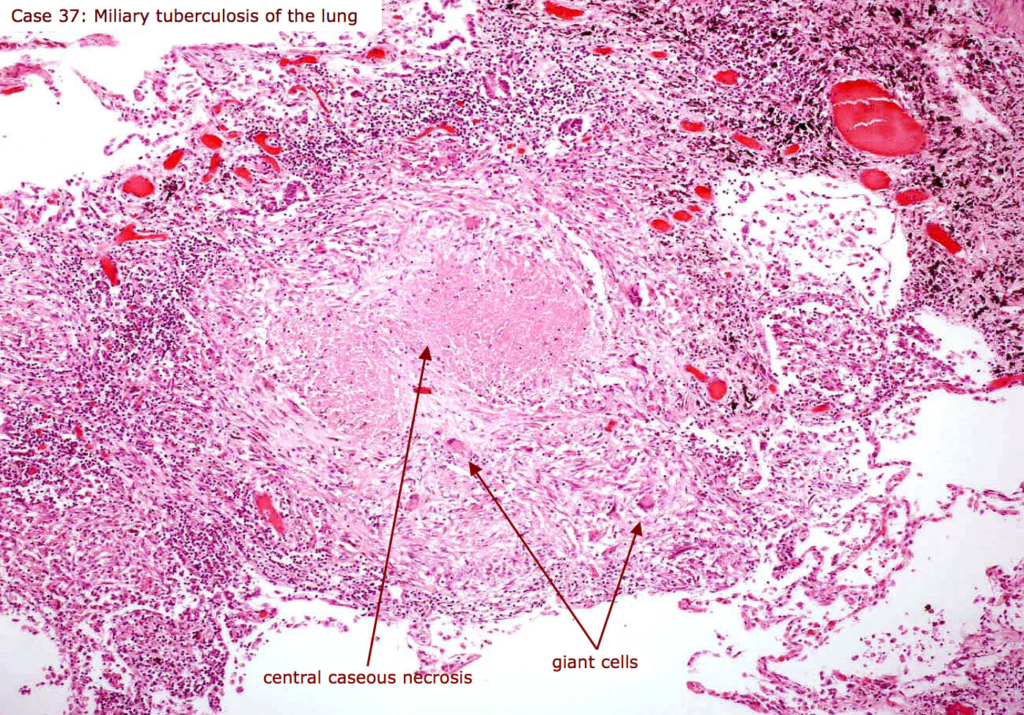
- caseous
- presence of fatty cell walled organisms creates a cheese-like consistency
- e.g.) tuberculosis, fungi
- presence of fatty cell walled organisms creates a cheese-like consistency
- fibrinoid
- result of protein leaking from vessel wall
- e.g.) blood vessels
- result of protein leaking from vessel wall
- gangrenous
- dry
- ischemic necrosis without concomitant bacterial infection
- wet
- liquefactive necrosis with concomitant bacterial infection
- dry
- coagulative


