Snapshot
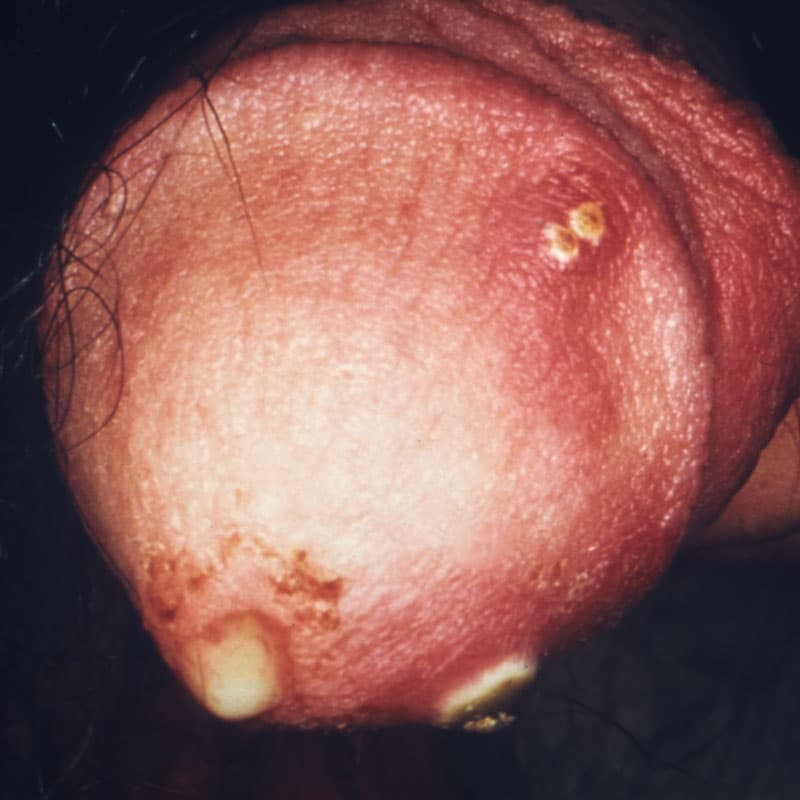
- 19-year-old male college student presents to the clinic complaining of a burning sensation with urination as well as purulent urethral discharge. He admits to rarely using condoms during sexual intercourse, and does not recall the last time he was tested for sexually-transmitted infections. Urinalysis is positive for leukocyte esterase and a Gram stain shows intracellular diplococci within polymorphonuclear neutrophils.
Introduction
- Classification
- Neisseria
- Gram-negative diplococci
- often intracellular within neutrophils
- Neisseria
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- the second most common bacterial sexually-transmitted infection (after Chlamydia)
- location
- genital tract
- risk factors
- unprotected sexual intercourse
- incidence
- Pathogenesis
- mechanism
- molecular biology
- pili facilitate attachment to mucosal surfaces
- antigenic variation
- IgA protease allows invasion of mucosal surfaces
- contains lipooligosaccharides (LOS) with strong endotoxin activity
- invasion of mucosal surfaces results in inflammation
- molecular biology
- transmission
- sexual
- perinatal
- mechanism
- Associated conditions
- septic arthritis
- neonatal conjunctivitis (2-5 days after birth)
- prophylaxis with erythromycin eye drops
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome
Presentation
- Symptoms
- dysuria
- purulent discharge
- fever
- prostatitis (men)
- endocervicitis (women)
- urethritis
Studies
- Labs
- Cervical and urethral culture
- Thayer-Martin agar
- selects for growth of Neisseria
- contains vancomycin, trimethoprim, colistin, and nystatin to inhibit growth of Gram-positive organisms, Gram-negative organisms except for Neisseria, and fungi
- Thayer-Martin agar
- Nucleic acid amplification testing (NAAT)
- Cervical and urethral culture
- Histology
- Gram stain of a cervical swab
- Gram-negative kidney-shaped diplococci
Differential
- Chlamydia
- distinguishing factor
- visualization of intracytoplasmic inclusions (reticulate bodies) on histology
- distinguishing factor
- Urinary tract infection
- distinguishing factor
- lack of growth on Thayer-Martin agar
- distinguishing factor
- Genital herpes simplex
- distinguishing factor
- painful vesicles and ulcers
Treatment
- Medical
- IM ceftriaxone
- add azithromycin or doxycycline for possible concomitant chlamydial infection
Complications
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
- may include salpingitis, endometritis, hydrosalpinx, tubo-ovarian abscess
- risk factor for ectopic pregnancy, infertility, chronic pelvic pain, and adhesions
- Fitz-Hugh-Curtis Syndrome
- perihepatitis
- infection and inflammation of liver capsule
- adhesions of peritoneum to liver
- perihepatitis
Comparison with N. meningitidis
| Characteristics | N. gonorrhoeae | N. meningitidis |
| Appearance | Kidney-bean shaped diplococci | |
| Oxidase test | Positive | |
| Polysaccharide capsule | No | Yes |
| Fermentation | Glucose (“Gonococci”) | Maltose and Glucose (“MeninGococci”) |
| Transmission | Sex | Respiratory |
| Vaccine | No (due to rapid antigenic variation) | Yes |
| β-lactamase production | Common | Rare |
| IgA protease production | Yes |


