Introduction
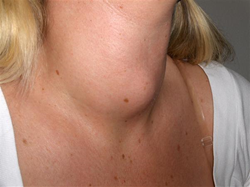
- Thyroid enlargement as a result of thyroid hormone deficiency
- initially, TH deficiency leads to uniform follicular epithelial hyperplasia as the thyroid gland attempts to compensate
- over time, thyroid architecture loses uniformity, leading to the areas of involution and fibrosis interspersed with areas of focal colloid hyperplasia
- Several types
- sporadic
- caused by puberty, pregnancy, enzyme deficiency
- sporadic
- Nontoxic means that the gland still depends on TSH stimulation
- goiter becomes toxic when hyperplasia becomes independent of TSH
Presentation
- Symptoms
- hoarseness
- due to compression of laryngeal nerve
- dyspnea
- due to compression of trachea
- hoarseness
- Physical exam
- diffuse thyromegaly (early)
- multinodular goiter (late)
- Pemberton’s sign
- compression of jugular vein leading to neck congestion
Treatment
- Pharmaceutic
- levothyroxine
Complications
- Hemorrhage into thyroid cyst
- presents as painful, rapid growth of a portion of the thyroid


