Overview
- Properties
- solubility
- lipophilic
- insoluble in plasma
- transportation
- must circulate bound to globulin proteins
- changes in amount of globulin hormone alter the free hormone level but does not alter the total hormone level
- free hormone level is what determines end organ effects
- speed of action
- slow due to time for transcription/translation
- solubility
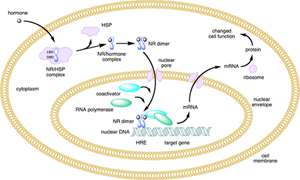
- Mechanism
- hormone binds to receptor in cytoplasm (sex hormones, cortisol, and aldosterone) or nucleus (thyroid) resulting in a conformation change allowing DNA binding
- in the case of steroid hormones via zinc finger motifs
- hormone-receptor complex binds to enhancer-like element in DNA
- gene transcription is stimulated
- hormone binds to receptor in cytoplasm (sex hormones, cortisol, and aldosterone) or nucleus (thyroid) resulting in a conformation change allowing DNA binding
- Examples
- progesterone
- estrogen
- testosterone
- cortisol
- aldosterone
- T3/T4


