Snapshot
- A 12-year-old boy presents to his pediatrician with right knee pain. He began playing basketball for his school a few months ago. On physical exam, there is a pronounced, tender tibial tubercle and tenderness to palpation over the affected area. The patient reports pain upon resisted knee extension.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- male:female ratio
- more common in males
- age bracket
- 12-15 years of age in boys
- 8-12 years of age in girls
- male:female ratio
- risk factors
- participating in sports
- demographics
- Pathogenesis
- Prognosis
- self-limiting
- responds well to conservative management
Presentation
- Symptoms
- anterior knee pain
- Physical exam
- inspection
- enlarged tibial tubercle
- tenderness over tibial tubercle
- provocative test
- inspection
- pain on resisted knee extension
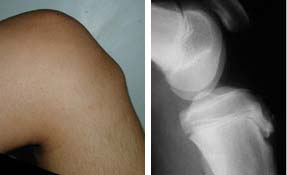
Imaging
- Radiographs
- recommended views
- lateral radiograph of the knee
- findings
- recommended views
- irregularity and fragmentation of the tibial tubercle
Studies
- Diagnostic criteria
- a clinical diagnosis
Differential
- Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndrome
- Osteochondroma of the proximal tibia
- Tibial tubercle fracture
- Patellar tendonitis
Treatment
- Conservative
- analgesics, ice, and physical therapy
- indication
- analgesics, ice, and physical therapy
- first-line treatment for Osgood-Schlatter disease
Complications
- Tubial tubericle prominence persists
- Genu recurvatum


