Collagen Vascular Disease
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- pleuritis + pleural effusions
- Rheumatoid arthritis (rheumatoid lung disease)
- pleuritis + pleural effusions
- also see pulmonary fibrosis (restrictive pattern)
- bilateral, diffuse appearance on chest radiograph
- progress to honeycomb lung in severe disease
- presentation
- gradual onset dyspnea
- end-inspiratory rales at lung base
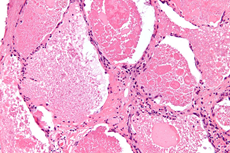
- lung biopsy shows patchy interstitial lymphoid infiltrate into walls of alveolar units
- NOT associated with rheumatoid nodules in the lung
- this finding is associated with Caplan’s syndrome (see Pneumoconioses )
- Systemic sclerosis (scleroderma)
- may also present with CREST syndrome (a variant of scleroderma)
- may lead to pulmonary hypertension and cor pulmonale
Iatrogenic Causes
- Drug-associated
- anti-cancer agents
- bleomycin/busulfan, methotrexate, nitrosourea, and cyclophosphamide
- anti-arrhythmics
- amiodarone
- anti-cancer agents
- Radiation-induced lung injury
- post-treatment pneumonitis (1-6 months following)
- associated with fever, dyspnea, and pleural effusions
- post-treatment pneumonitis (1-6 months following)
- dyspnea, nonproductive cough, fine crackles, and pulmonary fibrosis on chest radiograph
Occupational Causes
- Silicosis
- associated with occupational exposures of sandblasting, mining, and stone fabrication
- Silo filler’s disease
- hypersensitivity pneumonitis to nitrogen oxide gases released by plant matter
- Byssinosis
- hypersensitivity penumonitis to textile dusts (including cotton, hemp, and linen)
- Farmer’s lung
- hypersensitivity pneumonitis to Saccharopholyspora rectivirgula (thermophilic actinomyes)
- found in moldy hay
- type III hypersensitivity reaction with antigen-antibody complex depositing in lung
- hypersensitivity pneumonitis to Saccharopholyspora rectivirgula (thermophilic actinomyes)
- can become type IV hypersensitivity reaction with chronic exposure
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Introduction
- most common group of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia
- chronic alveolitis with no known cause
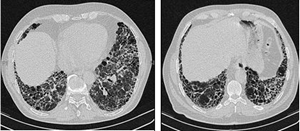
- persistent inflammation results in fibrosis (due to fibroblast proliferation) and cyst formation that is most prominent in subpleural regions (lower lung predominantly)
- typically seen in men 40-70 years old
- requires transplant at most advanced stages
- Presentation
- dyspnea on exertion most common symptom
- diagnosis can be made by HRCT if underlying causes excluded
- surgical lung biopsy shows usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP)
- Treatment
- Nintedanib
- receptor blocker of tyrosine kinases that mediate action of platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF)
- Pirfenidone
- Nintedanib
- inhibitor of transforming growth factor-beta (TGF-beta)
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis