- Oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve
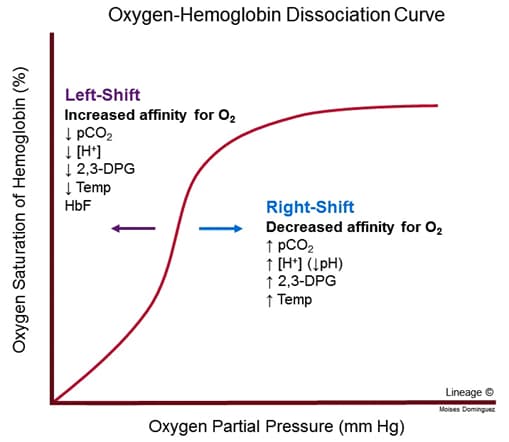
- sigmoidal shape is characteristic of positive cooperativity
- binding of 1 O2 molecule to 1 subunit of deoxyhemoglobin increases affinity for O2 in adjacent subunits
- P50 is PO2 at which hemoglobin is 50% saturated
- ↑ P50 → ↓ hemoglobin affinity for O2
- 50% saturation achieved at higher-than-normal P50
- ↓ P50 → ↑ hemoglobin affinity for O2
- 50% saturation achieved at lower-than-normal P50
- ↑ P50 → ↓ hemoglobin affinity for O2
- sigmoidal shape is characteristic of positive cooperativity
- Loading and unloading of oxygen
- in lungs
- PaO2 ≈ 100 mm Hg
- hemoglobin % saturation ≈ 100%
- facilitates maximal O2 loading into arterial blood in lungs
- in peripheral tissues
- PvO2 ≈ 40 mm Hg
- hemoglobin % saturation ≈ 75%
- facilitates O2 unloading into peripheral tissues
- in lungs
- Shift to right
- mechanism
- ↑ P50 → ↓ hemoglobin affinity for O2 → ↑ O2 unloading
- causes
- ↑ PCO2, ↓ pH (Bohr Effect)
- ↑ PCO2 → ↑ H+ → ↓ pH
- CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3–
- ↑ PCO2 → equilibrium reaction shifts right
- Le Chatelier’s principle
- ↑ PCO2 → equilibrium reaction shifts right
- CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3–
- ↑ CO2, ↑ H+ bind hemoglobin and stabilize low O2 affinity T (taut) state
- ↓ hemoglobin affinity for O2 → ↑ O2 unloading
- e.g., exercise → ↑ PCO2, ↓ pH
- ↑ O2 unloading ensures O2 delivery meets O2 demand in skeletal muscle
- e.g., exercise → ↑ PCO2, ↓ pH
- ↓ hemoglobin affinity for O2 → ↑ O2 unloading
- ↑ PCO2 → ↑ H+ → ↓ pH
- ↑ temperature
- e.g., ↑ tissue metabolism → ↑ temperature
- ↑ PCO2, ↓ pH (Bohr Effect)
- mechanism
- Shift to left
- mechanism
- ↓ P50→ ↑ hemoglobin affinity for O2 → ↓ O2 unloading
- causes
- ↓ PCO2, ↑ pH (Bohr Effect)
- ↓ PCO2 → ↓ H+ → ↑ pH
- ↓ CO2, ↓ H+ → stabilizes high O2 affinity R (relaxed) state
- ↑ hemoglobin affinity for O2 → ↑ O2 loading
- conversely, ↑ O2 decreases Hb affinity for CO2/H (Haldane effect)
- ↓ temperature
- ↓ tissue metabolism → ↓ temperature
- ↓ 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate (2,3-BPG)
- hemoglobin F
- fetal hemoglobin
- 2 α subunits and 2 γ subunits (α2γ2)
- ↑ affinity for O2, ↓ affinity for 2,3-BPG
- facilitates O2 delivery from mother to fetus
- ↑ affinity for O2, ↓ affinity for 2,3-BPG
- ↓ PCO2, ↑ pH (Bohr Effect)
- mechanism


