Hemoglobin
- Forms of O2 in Blood
- dissolved O2
- 2% of total O2 content
- O2 bound to hemoglobin
- 98% of total O2 content
- dissolved O2
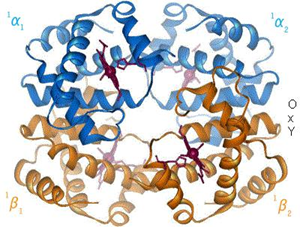
- Hemoglobin
- a globular protein conisisting of 4 polypeptide subunits
- 2 α subunits and 2 β subunits
- binds 4 O2 molecules
- each subunit contains a heme moiety (iron-binding porphyrin ring)
- iron in heme moieties is in reduced, ferrous state (Fe2+)
- Fe2+ binds O2 reversibly
- iron in heme moieties is in reduced, ferrous state (Fe2+)
- each subunit contains a heme moiety (iron-binding porphyrin ring)
- exists in 2 states
- low O2 affinity T (taut) state
- high O2 affinity R (relaxed) state
- R state has 300x greater affinity for O2
- exhibits positive cooperativity
- binding of 1 O2 molecule to 1 subunit of deoxyhemoglobin increases affinity for O2 in adjacent subunits
- a globular protein conisisting of 4 polypeptide subunits
- sigmoidal shape of oxygen-hemoglobin dissociation curve is characteristic of positive cooperativity
Hemoglobin Variants
- Hemoglobin F
- fetal hemoglobin
- 2 α subunits and 2 γ subunits (α2γ2)
- ↑ affinity for O2, ↓ affinity for 2,3-BPG
- facilitates O2 delivery from mother to fetus
- ↑ affinity for O2, ↓ affinity for 2,3-BPG
- Hemoglobin S
- an abnormal variant of hemoglobin that causes sickle cell disease
- α subunits are normal, β subunits are abnormal
- forms sickle-shaped robs in red blood cells in deoxygenated form
- distorts shape of red blood cells
- can result in occlusion of small blood vessels
- distorts shape of red blood cells
- ↓ affinity for O2
- an abnormal variant of hemoglobin that causes sickle cell disease


