Snapshot
- A 45-year-old woman presents with pain and achiness in her joints and bones, as well as confusion and a dulled mental state. She also has had recurrent episodes of kidney stones, and in the ED they found QTc shortening on her EKG. She is currently requesting morphine for her GI pain.
Introduction
- Associated with MEN I (parathyroid, pancreatic tumor, pituitary adenoma) and IIa (medullary carcinoma of the thyroid, pheochromocytoma, hyperplasia of the parathyroid)
- ret mutation
- Right inferior gland is most common location
- hyperactivity in one gland results in atrophy of remaining 3
- Carcinoma is rare
Presentation
Evaluation
- Histology
- sheets of chief cells
- no adipose tissue
- Serology
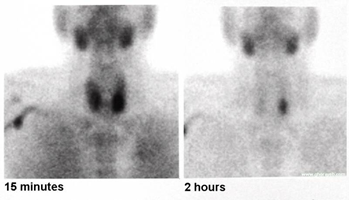
- Technetium-99m-sestamibi radionuclide scan
- localizes mass
Treatment
- Surgical
- adenoma excision
- hungry bones syndrome
- increased bone breakdown and leads to increased osteoblast activity in response to increased osteoclast activity from PTH
- when PTH decreases, osteoblast activity remains to rebuild the excess bone breakdown
- this causes hypocalcemia that is transient
- Chvostek’s sign
- Trosseau’s sign
- QTc lenthening
- this causes hypocalcemia that is transient
- hungry bones syndrome
- adenoma excision
- Acute hypercalcemia
- IV fluids
- loop diuretic (debatable as it can cause other electrolyte abnormalities)
- calcitonin
- bisphosphonate – long-term inhibition



