Introduction
PTH Pathway
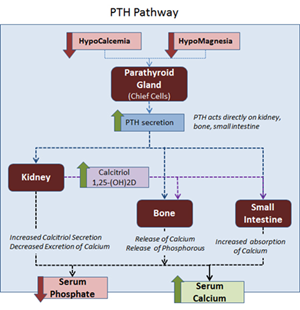
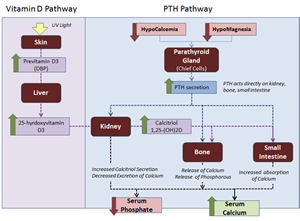
- Synthesis
- secreted by the chief cells of parathyroid
- responds to ionized calcium levels (physiologically-active), not total calcium levels (which includes physiologically-inactive calcium bound to protein)
- Function
- ↑ serum free Ca2+ and ↓ serum phosphate in response to hypocalcemia/hypomagnesemia via
- ↑ bone resorption of calcium and phosphate (bone is destroyed)
- PTH receptor is on the osteoblasts secretes IL-1 to activate osteoclasts via production of M-CSF and RANK-L
- PTH decreases osteoprotegrin (OPG), decoy receptor for RANKL, thereby resulting in an increased interaction between RANKL and osteoclasts
- ↑ kidney resorption of calcium in distal convoluted tubule
- ↓ kidney resorption of phosphate (increasing urine phosphate)
- ↑ bone resorption of calcium and phosphate (bone is destroyed)
- ↑ serum free Ca2+ and ↓ serum phosphate in response to hypocalcemia/hypomagnesemia via
- ↑ 1,25-(OH)2 vitamin D production (via 1 alpha-hydroxylase)
Clinical Conditions



