Snapshot
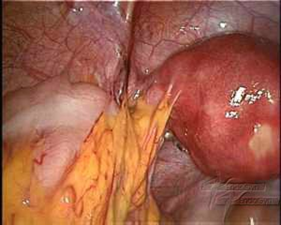
- A sexually active 17-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department due to lower abdominal pain of acute onset. She has no nausea or vomiting. Vital signs are significant for a temperature of 101.4°F (38.5°C). Bimanual pelvic exam shows cervical exudate and cervical motion tenderness. There is bilateral lower quadrant tenderness. Her β-HCG is within normal limits.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the upper female genital tract that is often polymicrobial
- may include
- endometritis
- salpingitis
- tubo-ovarian abscess
- pelvic peritonitis
- may include
- pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is an infection of the upper female genital tract that is often polymicrobial
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- US incidence
- 750,000 cases annually
- US incidence
- demographics
- sexually active women
- 15-29 years of age
- location
- upper female genital tract
- risk factors
- age < 25 years of age
- risky sexual behavior
- earlier age at first intercourse
- increasing number of sex partners
- incidence
- Pathophysiology
- pathobiology
- usually polymicrobia
- likely microbes
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- anaerobes
- gram-negative rods
- Streptococcus agalactiae
- Gardnerella vaginalis
- Haeomphilus influenza
- Cytomegalovirus
- Mycoplasma genitalium
- pathoanatomy
- ascending infection of microbes from endocervix to upper genital tract
- pathobiology
- Associated conditions
- other sexually transmitted diseases (e.g., chlamydia, chancroid, herpes, etc.)
- Prognosis
- may recur
- prognostic variable
- negative
- salpingitis
- negative
- multiple recurrence
Presentation
- Symptoms
- may be asymptomatic if subclinical
- primary symptoms
- lower abdominal or pelvic pain
- chills
- dyspareunia
- dysuria
- nausea or vomiting
- Physical exam
- inspection
- fever
- abnormal cervical discharge or bleeding
- cervical friability
- abnormal vaginal odor
- ecchymosis and swelling
- diffuse tenderness
- provocative tests
- cervical motion tenderness
- also known as “chandelier test”
- adnexal tenderness
- cervical motion tenderness
- inspection
- uterine tenderness
Imaging
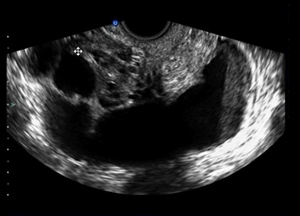
- Ultrasonography
- indication
- if diagnosis is uncertain with physical exam and clinical history
- view
- transvaginal
- findings
- thickened fluid-filled tubes
- with or without free pelvic fluid
- indication
- with or without tubo-ovarian abscess
Studies
- Labs
- may test positive for sexually transmitted diseases
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- may test positive for sexually transmitted diseases
- Diagnostic criteria
- positive physical exam findings
- uterine tenderness
- adnexal tenderness
- positive physical exam findings
- cervical motion tenderness
Differential
- Ectopic pregnancy
- positive pregnancy test
- Appendicitis
- PID typically presents with bilateral abdominal tenderness
Treatment
- Medical
- cephalosporin plus doxycycline (outpatient)
- indications
- clinical findings of PID alone is often enough to indicate treatment of PID
- uncomplicated PID
- indications
- cefoxitin plus doxycycline
- indications for intravenous medication or hospitalization
- uncertain diagnosis
- tubo-ovarian abscess
- unstable patient
- indications for intravenous medication or hospitalization
- cephalosporin plus doxycycline (outpatient)
- failure to respond to outpatient treamtment within 72 hours
Complications


