Snapshot
- A 29-year-old G2P1 female presents to labor and delivery triage with bleeding in the third trimester. Her first pregnancy was a cesarean delivery delivered at 37 weeks. She describes her bleeding as painless spotting without abdominal pain. An urgent transabdominal ultrasound is performed, showing a viable fetus and normal amniotic fluid. A transvaginal ultrasound is subsequently performed, and shows the placental edge located 1cm from the internal cervical os.
Introduction
- Overview
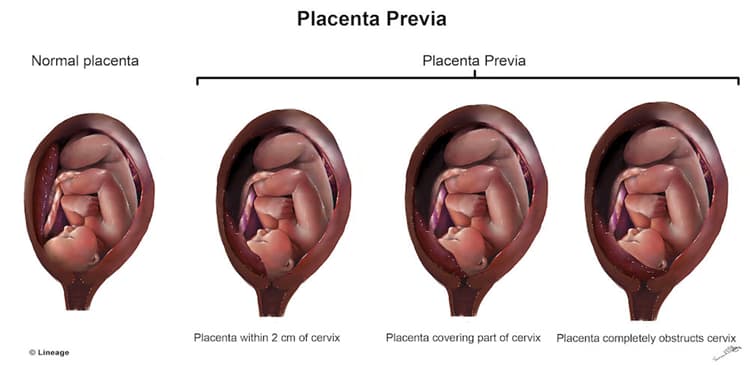
- placenta previa is a condition characterized placental tissue extending over or < 2 cm from the internal cervical os and is associated with painless third trimester bleeding
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- occurs in approximately 1 per 250 births
- incidence
- Associated conditions
- placenta previa-accreta spectrum
- placenta previa is present along with placenta accreta, placenta increta, or placenta percreta
Presentation
- Most common presentation is asymptomatic finding on routine ultrasound at 16-20 weeks of gestation
- Symptoms
- uterine contractions, pain, and bleeding
- 10-20% of cases
- uterine contractions, pain, and bleeding
- Physical exam
- digital vaginal examination is contraindicated until placenta previa is excluded (may result in severe hemorrhage)
- findings may include the following
- hemorrhage
- usually spontaneously ceases after 1-2 hours
- hypotension
- tachycardia
- hemorrhage
- usually no fetal distress (in contrast with vasa previa)
Imaging
- Ultrasonography
- transvaginal ultrasound
- gold standard for diagnosis of placenta previa
- transabdominal ultrasound
- can be used as a screening test or in conjunction with transvaginal ultrasound
- transvaginal ultrasound
- if distance between edge of placenta and cervical os is ≤ 2 cm on transabdominal ultrasound, perform transvaginal ultrasound to better visualize placental position
Studies
- Rh compatability test
- Complete blood cell (CBC) count
- Prothrombin time (PT) and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
- Blood type and cross
- Levels of fibrin split products (FSP) and fibrinogen
Differential
- Abruptio placentae
- key distinguishing factors
- placenta prematurely separates from the uterine wall
- presents with painful bleeding that does not spontaneously cease
- key distinguishing factors
- Placenta accreta
- key distinguishing factors
- placenta invades the uterine wall
- placenta does not separate after delivery, which may lead to postpartum bleeding
- key distinguishing factors
- Vasa previa
- key distinguishing factors
- fetal vessels extend over the internal cervical os
- key distinguishing factors
- presents with fetal heart decelerations due to compression of umbilical vessels
Treatment
- Medical
- monitoring
- in the case of asymptomatic placenta previa
- monitor placental position
- determine whether placenta accreta is also present
- if persistent placenta previa, plan for cesarean delivery
- in the case of asymptomatic placenta previa
- hemostasis
- in the case of actively bleeding placenta previa
- admit for maternal and fetal monitoring
- achieve and maintain maternal hemodynamic stability
- in the case of actively bleeding placenta previa
- monitoring
- Surgical
- cesarean delivery
- cesarean delivery should be performed in these cases
- active labor
- fetal distress (category III fetal heart rate tracing that does not respond to in utero resuscitation)
- inability to achieve maternal hemodynamic stability
- cesarean delivery should be performed in these cases
- cesarean delivery
- significant vaginal bleeding after 34 weeks of gestation
Complications
- Congenital malformations
- associated with 2-fold increase
- Fetal malpresentation
- Vasa previa
- rupture of fetal vessels that cross the membranes covering the cervix
- cesarean delivery indicated
- Postpartum hemorrhage



