Overview
- Fertilization and implantation
- ovum is fertilized in ampulla of Fallopian tube several hours after ovulation
- blastocyst implants in endometrium 6 to 7 days after ovulation
- syncytiotrophoblast cells secrete hCG that rescues corpus luteum
- hCG
- in first trimester,hCG sustains corpus luteum in presence of falling LH levels
- corpus luteum produces progesterone
- progresterone is necessary for maintenance of pregnancy
- corpus luteum produces progesterone
- hCG levels detectable in blood (1 week post-conception)
- hCG levels detectable in urine (2 weeks post-conception)
- e.g., home pregnancy test
- in first trimester,hCG sustains corpus luteum in presence of falling LH levels
- in second and third trimesters, placenta produces estrogen and progesterone
- corpus luteum degenerates
- hCG levels elevated in certain pathologies
- hydatidiform moles
- choriocarcinoma
- Lactation
- post-delivery, ↓ progesterone levels, prolactin promotes lactation
- initiation of milk production by alveolar cells
- post-delivery, ↓ progesterone levels, prolactin promotes lactation
- Suckling
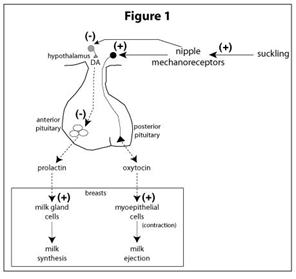
- stimulates sensory nerves that carry suckling signal from breast to hypothalamus via spinal cord, a process that mediates prolactin and oxytocin release
- Prolactin
- suckling sends signal from breast (nipple) to hypothalamus
- suckling input in arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus inhibits dopamine release
- dopamine travels via hypothalamic-portal system to anterior pituitary to inhibit prolactin (PRL) release by lactotrophs
- suckling inhibits release of dopamine and causes ↑ PRL
- suckling input in arcuate nucleus of hypothalamus inhibits dopamine release
- prolactin promotes lactation and maintains lactation once established
- suckling sends signal from breast (nipple) to hypothalamus
- Oxytocin
- suckling sends signal from breast (nipple) to hypothalamus
- suckling input in supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei of hypothalamus triggers oxytocin release via posterior pituitary
- oxytocin promotes contraction of myoepithelial cells → promotes milk letdown
- suckling sends signal from breast (nipple) to hypothalamus
- Relaxin
- leads to sacroiliac joint laxity and widening of the pubic symphysis in preparation for delivery
- Physiologic changes
- increased red blood cell mass
- increased plasma volume
- increased cardiac output
- decreased vascular resistance
- mild respiratory alkalosis due to increased tidal volume
- hypercoagulability


