Snapshot
A 62-year-old man presents to his primary care physician complaining of constant itchings and yellow skin and eyes. On exam, there is no evidence of hepatomegaly, however, laboratory findings are of concern for elevated serum ALP and GGT.
Introduction
- Chronic cholestatic syndrome characterized by fibrosing inflammation in the intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile duct
- onset usually insidious
- leads to narrowing and, eventually, obliteration of the bile ducts
- Cause of primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) is unknown
- PSC occurs most often in
- young men (< 50 years old)
- HLA-DR52a positive
- commonly associated with inflammatory bowel disease
- especially ulcerative colitis
Presentation
- Symptoms
- pruritus
- jaundice
- some present with hepatosplenomegaly or features of cirrhosis
Evaluation
- Labs
- ↑ serum ALP, GGT
- bilirubin ↑ with conjugated fraction > 50%
- typical of obstructive pattern
- no urine urobilinogen
- low urine urobilin
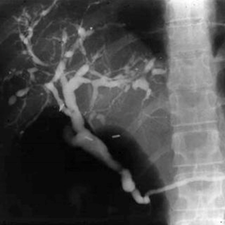
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiography (ERCP)
- give the biliary tree an irregular beaded appearance
Treatment
- Liver transplantation
- prior to liver failure is a possibility in selected cases
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- Prognosis is poor
- May result in liver failure, cirrhosis, cholangiocarcinoma



