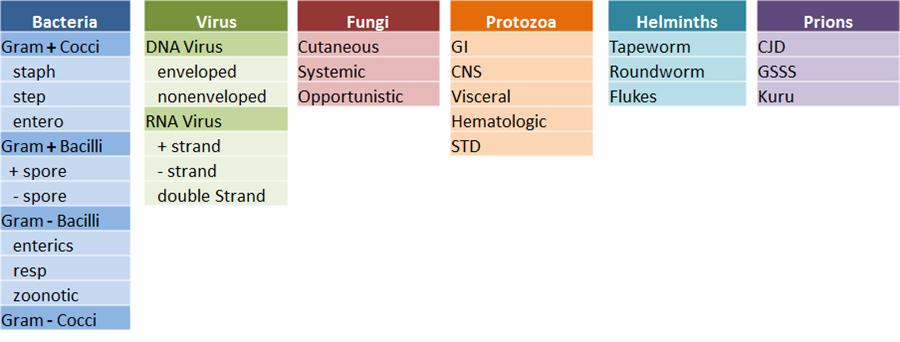
Microbiology Overview
Prion Introduction
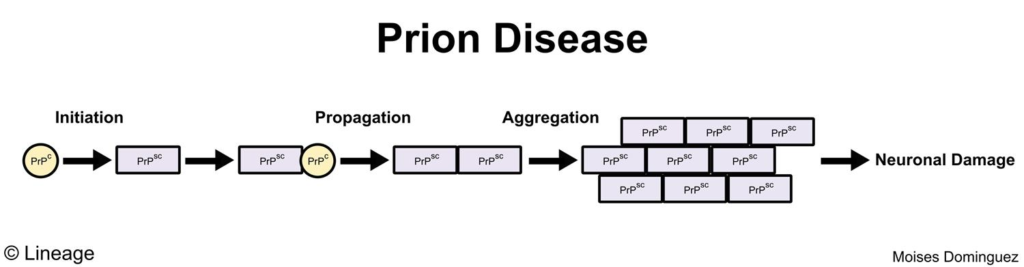
- A prion is an infective protein
- prions are the only known infectious agents that do not contain DNA or RNA
- when prions infect an organism, they cause normal proteins to misfold and assume the infectious prion form
- proteins accumulate in the infectious form causing disease
- The prion protein (PrP) is the particular protein that is implicated in all prion diseases
- normal PrP is denoted PrPC
- in prion diseases, PrP is misfolded and denoted PrPSc
- PrPSc forms amyloid aggregates containing β-pleated sheets
- Prion diseases
- in all prion diseases, the accumulation of PrPSc results in
- spongiform encephalopathy
- dementia
- ataxia
- death
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- rapidly progressive dementia
- human form of “mad cow disease” (“variant” CJD)
- Gerstmann-Sträussler-Scheinker syndrome
- genetic alteration in PrP
- inherited
- kuru
- cannibalism in Papua New Guinea
- in all prion diseases, the accumulation of PrPSc results in



