Overview
Snapshot
- A 32-year-old previously healthy man develops headache, fatigue, vomiting, and shortness of breath about 12 hours after arriving to Mt. Everest Base Camp. Over the next day, he develops mild difficulty walking, and confusion. He is seen by a physician who administers a medication and advises him to rest. His symptoms improve over the next 24-48 hours. (Acetazolamide)
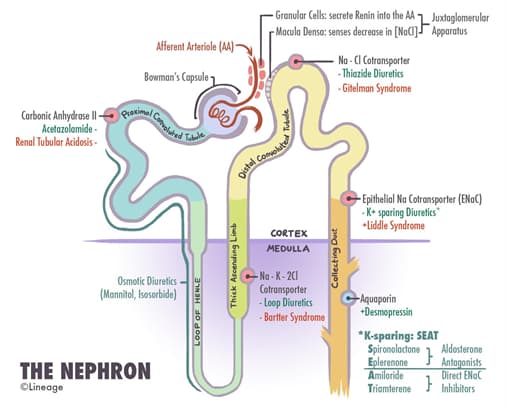
Mannitol
- Mechanism
- osmotic diuretic
- increases osmotic pressure of the glomerular filtrate
- this in turn impairs tubular reabsorption of water and electrolytes
- increases osmotic pressure of the glomerular filtrate
- osmotic diuretic
- Clinical use
- oliguria
- which can result from shock and trauma
- drug overdose
- promotes urinary excretion of toxic substances
- glaucoma
- ↓ intraocular pressure
- increased intracranial pressure
- especially in the setting of cerebral edema
- oliguria
- Toxicity
- congestive heart failure (CHF) exacerbation
- hypovolemia
- Contraindications
- anuria
- CHF
Acetazolamide
- Mechanism
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
- blocks reabsorption of bicarbonate
- dissociation of carbonic acid into water and carbon dioxide in the proximal tubule prevented
- bicarbonate in the lumen then binds to sodium to form sodium bicarbonate which is excreted
- blocks reabsorption of bicarbonate
- results in sodium bicarbonate diuresis and ↓ total body bicarbonate
- loss of bicarbonate results in metabolic acidosis
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitor
- Clinical use
- glaucoma
- urinary alkalinization
- metabolic alkalosis
- altitude sickness
- increased intracranial pressure
- especially for idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- Toxicity
- hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis (non-anion gap)
- type 2 renal tubular acidosis
- hypokalemia
- neuropathy/parasthesias
- ↑ renal stone production
- calcium phosphate stones
- ammonia toxicity
- sulfa allergy



