Snapshot
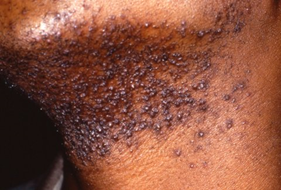
- A 16-year-old African American boy presents to his pediatrican’s office for razor bumps. He started shaving 2 years ago and has had intermittent rashes after shaving. He reports that the rash is both itchy and painful but seems to improve if he stops shaving. On physical exam, he has clusters of hyperpigmented firm papules along his jawline. Some papules have visible loops of short hair penetrating the skin with surrounding erythema. He is given low potency topical steroids and counseled on other methods of hair removal.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- male > female (due to beard area)
- often affects African Americans
- risk factors
- shaving
- tightly curled hair
- demographics
- Pathogenesis
- pseudofolliculitis barbae is NOT a true folliculitis
- entrapment of short hairs causes inflammatory response
Presentation
- Symptoms
- skin lesions are painful and pruritic
- Physical exam
- firm and skin-colored or hyperpigmented papules and pustules
- there may be loops of hair emerging from the follicular orifice
- firm and skin-colored or hyperpigmented papules and pustules
- located on cheeks, jaw, or neck (in hair-bearing areas)
Studies
- Labs
- none
- Biopsy
- not necessary unless clinical diagnosis is unclear
- Histology
- intraepidermal neutrophils
- abscess formation in dermis
- granulomatous inflammation with foreign-body giant cells around the penetrating hair
Differential
- Folliculitis
- Cutaneous sarcoidosis
- does not have embedded hairs and lesions may be outside of hair-bearing areas
Treatment
- Conservative
- other methods of hair removal
- indication
- as a shaving alternative as this causes pseudofolliculitis barbae
- modalities
- depilatory hair removal
- laser hair removal
- waxing
- indication
- other methods of hair removal
- Medical
- topical therapy
- indication
- to reduce symptoms
- drugs (all topical)
- retinoids
- corticosteroids
- antibiotics
- eflornithine
- indication
- topical therapy
- alpha-hydroxy acids (chemical exfoliants)
Complications
- Scarring or keloid formation
- Secondary bacterial infection


