Snapshot
- A 32-year-old man presents to his rheumatologist for evaluation of new-onset joint pain. He reports feeling stiffness in his lower back in the morning and in the most distal joints in his left hand. He has a past medical history of psoriasis. On physical exam, he has papules and plaques along his hairline and scalp with overlying silver scales. His left middle finger has dactylitis and the distal interphalangeal joint is swollen. Laboratory evaluation shows that he is seronegative for rheumatoid factor. He is started on apremilast.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- a seronegative spondyloarthritis associated with skin psoriasis
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- < 1% of population
- 20-30% of patients with psoriasis
- demographics
- peak incidence in 30-50 years of age
- risk factors
- scalp psoriasis
- nail lesions in psoriasis
- incidence
- Etiology
- idiopathic
- Pathogenesis
- ↑ interferon-α, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-α, and other inflammatory markers recruit T-cells into skin and joints
- osteoclasts are exposed to inflammatory molecules in the psoriatic joint, triggering osteoclast activation and causing osteolysis
- Associated conditions
- skin psoriasis
- other HLA-B27 autoimmune diseases
Presentation
- Symptoms
- asymmetric joint involvement
- often distal interphalangeal joint (DIP)
- spine can be involved
- joint pain
- joint stiffness in the morning
- asymmetric joint involvement
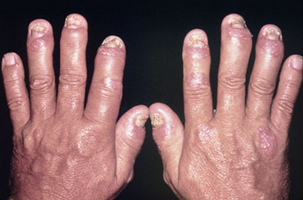
- Physical exam
- swelling in the affected joints
- in particular the hands > feet
- psoriatic lesions
- sharply demarcated pink plaque with silvery scale
- pitting nails
- uveitis
- swelling in the affected joints
- sacroiliitis
Imaging
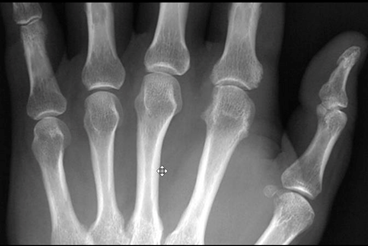
- Radiographs
- indications
- to confirm diagnosis
- recommend views
- affected joints
- findings
- bone proliferation and bone resorption
- pencil-in-cup deformity of DIP, demonstrating erosive changes
- indications
- this is distinct from rheumatoid arthritis
Studies
Differential
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- metacarpal phalangeal joint involvement, not DIP
Treatment
- Conservative
- weight loss
- indications
- for patients who are overweight
- may reduce disease activity in psoriatic arthritis
- indications
- weight loss
- Medical
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- indication
- first-line therapy for mild joint symptoms
- indication
- disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
- indication
- if patients have > 5 joints involved, radiographic damage, or elevated inflammatory markers
- drugs
- methotrexate
- leflunomide
- sulfasalazine
- apremilast
- tumor necrosis factor-α inhibitors
- anti-interleukin agents
- ustekinumab
- indication
- nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- secukinumab
Complications
- Cardiovascular disease


