Snapshot
- A 22-year-old man presents to his primary care physician’s office due to pain in his knee, dysuria, and eye discomfort and discharge. Medical history is significant for a sexually transmitted infection due to Chlamydia approximately 1 month ago. On physical exam, there is conjunctivitis, left-knee swelling and tenderness, and urethral discharge.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- a systemic inflammatory disorder that results from following an extra-articular infection (e.g., sexually transmitted infection and gastroenteritis)
- typically results after 1-6 weeks after the infection
- formerly known as Reiter syndrome
- classic triad is
- urethritis
- conjunctivitis
- arthritis
- a systemic inflammatory disorder that results from following an extra-articular infection (e.g., sexually transmitted infection and gastroenteritis)
- Epidemiology
- demographics
- age
- 20-40 years of age
- sex
- following a genitourinary infection, it is more common to develop reactive arthritis in men
- affects men and women equally a gastrointestinal infection
- age
- demographics
- Etiology
- genitourinary pathogens
- Chlamydia trachomatis
- gastrointestinal pathogens
- Salmonella enteritidis and typhimurium
- Shigella
- Yersinia
- Campylobacter
- genitourinary pathogens
- Pathogenesis
- unclear
- Prognosis
- most cases spontaneously recover
Presentation
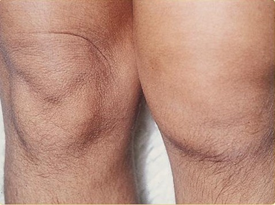
- Symptoms
- asymmetric joint pain
- e.g., knee, ankle, and heel
- eye discomfort
- in cases of conjunctivitis
- asymmetric joint pain
- Physical exam
- conjunctivitis
- arthritis
- typically an acute and asymmetric oligoarthritis
- genital involvement
- circinate balanitis
- urethritis
- cervicitis
- keratoderma blennorrhagicum
Studies
- Labs
- complete blood count
- may demonstrate
- neutrophillic leukocytosis
- may demonstrate
- ↑ C-reactive protein (CRP) and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- complete blood count
- Diagnostic criteria
- a clinical diagnosis
Differential
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Enteropathic arthritis
- Septic arthritis
- Gonococcal arthritis
- Gout
- Pseudogout
- Rheumatoid arthritis
Treatment
- Medical
- nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
- indication
- drug of choice for acute phase of reactive arthritis
- indication
- nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)


