Overview
Introduction
- Most small substances are freely filtered by the glomerulus meaning
- filtration is in general a non-selective process
- a diverse set of substances enter the proximal tubule
- Substances are subsequently secreted or reabsorbed by the proximal tubule so that
- toxins can be cleared faster than filtration alone would allow
- useful substances can be retained by the body despite filtration
- The balance between secretion and reabsorption of each substance controls
- the concentration of that substance at the end of the proximal tubule
- the concentration that is presented to downstream portions of the nephron
- The proximal tubule also absorbs the majority of filtered water
Relative Tubular Concentrations
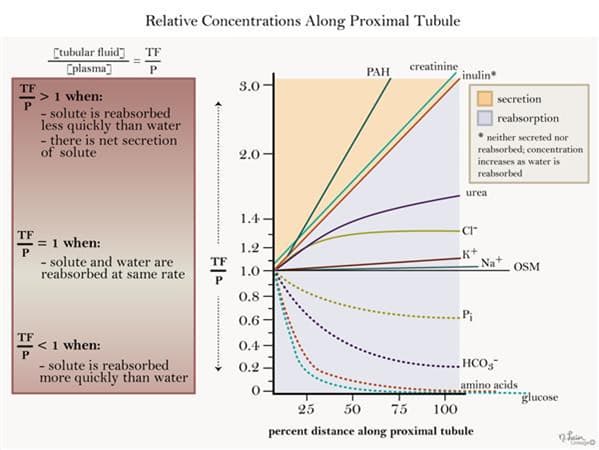
- Substance concentrations in the proximal tubule can be defined relative to the plasma concentration of the same substance (tubular fluid/plasma = TF/P) so that
- the action of the proximal tubule on the substance can be easily determined
- substances can be analyzed relative to those with known behavior
Key Proximal Tubule Changes
- Inulin is neither secreted nor reabsorbed in the proximal tubule so
- it ↑ in concentration along the proximal tubule
- its concentration can be viewed as a proxy for water reabsorption
- Na+ reabsorption is the main driver of H2O reabsorption so
- sodium TF/P remains close to 1 throughout the proximal tubule
- Cl– reabsorption has two phases including a
- slower rate than Na+ in the proximal 1/3 of the proximal tubule
- equivalent rate to Na+ in the rest of the proximal tubule
- Cl– TF/P therefore ↑ before it plateaus


