Snapshot
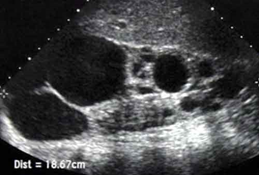
- A 26-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with abdominal and lower back pain. He reports to also seeing blood in his urine. Medical history is non-contributory. Family history is significant for his father requiring hemodialysis at a young age. Vitals signs are significant for a blood pressure of 162/112 mmHg. A renal ultrasound is performed and shown. (Adult polycystic kidney disease)
Adult Polycystic Kidney Disease (ADPCKD)
- Clinical definition
- an inherited disorder that results in expansion of multiple renal cysts which ultimately leads to end-stage renal disease
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- the most common inherited cause of kidney disease
- demographics
- ≥ 30 years of age
- risk factors
- family history
- incidence
- Pathogenesis
- PKD1 or PKD2 mutations results in abnormal cell signaling that results in cystogenesis
- expansion of cysts results in progressive loss of nephrons
- PKD1 or PKD2 mutations results in abnormal cell signaling that results in cystogenesis
- Genetics
- inheritance pattern
- autosomal dominant
- inheritance pattern
- Associated conditions
- cyst development in other organs such as
- liver (most common extra-renal cyst type)
- pancreas
- seminal vesicle
- cardiovascular abnormalities
- mitral valve prolapse
- left ventricular hypertrophy
- diverticulosis
- cyst development in other organs such as
- Prognosis
- with age the number and size of the cyst increases
- Presentation
- symptoms
- abdominal or flank pain
- low back pain
- hematuria
- recurrent urinary tract infections
- symptoms
- hypertension
Juvenile Polycystic Kidney Disease (ARPCKD)
- Clinical definition
- a congenital fibrocystic disorder that results in renal and hepatic manifestations
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- 1 in 20,000 live births
- incidence
- Pathogenesis
- PKHD1 gene mutation leads to abnormal production of fibrocystin and polyductin which results in defects of the
- renal tubular structures
- dilatation and elongation of collecting ducts
- bile duct structures
- cystic dilatation of intra- and extra-hepatic bile ducts
- renal tubular structures
- PKHD1 gene mutation leads to abnormal production of fibrocystin and polyductin which results in defects of the
- Genetics
- inheritance pattern
- autosomal recessive
- inheritance pattern
- Associated conditions
- Presentation
- symptoms/physical exam
- bilateral abdominal mass in infants and children
- hepatomegaly in infants and children
- symptoms/physical exam
- hypertension
Medullary Cystic Disease
- Clinical definition
- medullary cystic disease is characterized by
- autosomal dominant inheritance pattern
- progressive and slow impairment in renal function that ultimately results in end-stage renal disease
- no or minimal proteinuria with a bland urine sediment
- medullary cysts on renal ultrasound
- in most cases medullary cysts are not present
- can see shrunken kidneys on ultrasound
- medullary cystic disease is characterized by


