Overview
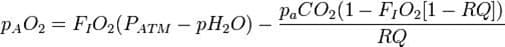
- High altitude → ↓ atmospheric pressure (Patm) and ↓ alveolar PO2
- Ventilation
- Arterial blood
- ↑ ventilation rate → ↑ PaO2 and ↓ PaCO2 → respiratory alkalosis
- CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3–
- ↓ CO2 shifts equilibrium left
- ↓ H+→ ↑ pH
- ↓ CO2 shifts equilibrium left
- CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 → H+ + HCO3–
- respiratory alkalosis → ↑ renal HCO3– excretion
- carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., acetazolamide) → ↑ renal HCO3– excretion and create a metabolic acidosis, which can be used to “acclimate” someone going to a higher altitude because they will naturally increase ventilation to compensate for metabolic acidosis
- ↑ ventilation rate → ↑ PaO2 and ↓ PaCO2 → respiratory alkalosis
- Pulmonary blood flow
- ↓ alveolar PO2 → hypoxic vasoconstriction of pulmonary vasculature → ↑ pulmonary vasculature resistance → ↑ pulmonary arterial pressure
- pulmonary arterial pressure increases to maintain a constant blood flow
- right ventricle pumps against ↑ pulmonary arterial pressure (↑ afterload)
- chronic hypoxic vasoconstriction of pulmonary vasculature causes cor pulmunale (right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH))
- right ventricle pumps against ↑ pulmonary arterial pressure (↑ afterload)
- pulmonary arterial pressure increases to maintain a constant blood flow
- ↓ alveolar PO2 → hypoxic vasoconstriction of pulmonary vasculature → ↑ pulmonary vasculature resistance → ↑ pulmonary arterial pressure
- Cerebral blood flow
- primarily controlled by PCO2
- ↓ PCO2 → vasoconstriction
- therapeutic hyperventilation (↓ PCO2) → ↓ intracranial pressure by decreasing cerebral perfusion
- used in cases of cerebral edema
- effect is usually only temporary
- PO2 can have effects during severe hypoxic events
- ↓ PO2 → vasodilation and ↑ cerebral perfusion pressure
- primarily controlled by PCO2
- Cellular changes
- chronic hypoxia → ↑ erythropoietin → ↑ hemoglobin concentration and ↑ hematocrit
- synthesis of erythropoietin in kidneys
- erythropoietin acts on bone marrow to stimulate RBC synthesis
- ↑ hemoglobin concentration → ↑ O2 carrying capacity and ↑ total O2 content
- synthesis of erythropoietin in kidneys
- ↑ mitochondria
- chronic hypoxia → ↑ erythropoietin → ↑ hemoglobin concentration and ↑ hematocrit
- Oxygen-hemoglobin dissocation curve
- ↑ 2,3-BPG → shifts to right
- ↓ hemoglobin affinity for O2 → ↑ O2 unloading
- ↑ 2,3-BPG → shifts to right


