Snapshot
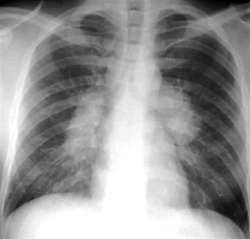
- A previously healthy 30-year-old African American woman has fatigue, arthralgia, and a nodular rash over the trunk and upper extremities for three weeks. There are twelve 3-8 mm, pale, indurated plaques over the chest, back, and upper extremities. The liver is palpable 2 cm below the right costal margin with a percussion span of 14 cm, and the spleen tip is palpable 3 cm below the left costal margin. There is no pain or limitation of any of the joints. A chest radiograph shows bilateral lymphadenopathy.
Introduction
- Idiopathic condition characterized by granulmomatous inflammation of multiple organs
- lungs most commonly involved organ
- commonly causes restrictive lung disease
- may also cause obstructive or mixed pattern
- granulomas can affect all organ systems
- liver/spleen
- bone
- heart
- Epidemiology
- most common in black females
- smoking does not ↑ risk
- presents most commonly in 3rd or 4th decade
- Associated conditions
- diabetes insipidus (granulomatous infiltration of posterior pituitary)
Presentation
- Symptoms
- may be asymptomatic
- 50% as incidental chest radiograph findings
- cough
- fever, malaise
- arthritis
- symptoms mainly in the ankle and legs
- can be GRUELING
- Granulomas
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Uveitis
- Erythema nodosum
- Lymphadenopahy
- Interstitial fibrosis
- Negative TB
- Gammaglobulinemia
- may be asymptomatic
- Physical exam
- skin lesions
- nodular granulomatous lesions
- facial rash
- skin lesions
- enlarged salivary and lacrimal glands
Evaluation
- Diagnosis is clinical and often one of exclusion
- Chest radiograph
- bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
- lungs involved in 90% of the cases
- Labs
- hypercalcemia
- ↑ 1-α-hydroxylase → hypervitaminosis D
- can cause hypercalemia and renal failure chronically
- commonly tested, less commonly seen (only about 11%)
- ↑ 1-α-hydroxylase → hypervitaminosis D
- serum protein electrophoresis (SPE) shows polyclonal gammopathy
- lack of response to CD4 TH skin tests (like PPD) due to ↑ lung activity and ↓ systemic activity
- hypercalcemia
- Pulmonary function tests
- restrictive pattern is common (normal FEV1/FVC with normal TLC)
- however, obstructive or mixed pattern may also be seen
- restrictive pattern is common (normal FEV1/FVC with normal TLC)
- Bronchoalveolar lavage
- Biopsy
- laminated calcium concretions present (cause of density on CXR)
Treatment
- Conservative
- observationfine in most cases
- majority experience remission within two years without treatment
- observationfine in most cases
- Pharmacologic
- topical preferred when possible (skin, eyes, nasal, airway, etc)
- corticosteroids
- indications
- extra-pulmonary manifestations: cardiac, neurologic, or uveitis
- symptomatic hepatosplenomegaly
- significant hypercalcemia
- only if refractory to observations
Prognosis
- Relapsing/remitting course with 50% resolving spontaneously
- Progression
- Stage I – bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy
- Stage II – bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy + upper lobe infiltrates
- Stage III – lung infiltrates only
- Stage IV – lung fibrosis


