Snapshot
- A 50-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician’s office for persistently dry eyes and mouth. She reports that this started several months ago and has not improved. She has been using artificial tears for the past few weeks without much relief. She also reports feeling very tired and anxious. She has a past medical history of systemic lupus erythematosus and a family history of rheumatoid arthritis. Physical exam reveals dry mucous membranes, swollen parotid glands, and conjunctivitis on exam. She is prescribed pilocarpine and sent for an autoimmune workup.
Introduction
- Clinical definition
- an autoimmune disease of the exocrine glands
- Epidemiology
- prevalence
- relatively common (up to 5% prevalence)
- demographics
- female > male
- 40-60 years of age
- second most common autoimmune rheumatic disease
- risk factors
- family history
- comorbid autoimmune disease
- prevalence
- Pathogenesis
- associated with HLA-DR52
- environmental trigger, such as a viral infection, may cause
- inflammatory destruction of exocrine glands and is characterized by aggregation of lymphocytes, primarily CD4+ T-cells and memory cells
- the salivary and lacrimal glands are most commonly affected
- inflammatory destruction of exocrine glands and is characterized by aggregation of lymphocytes, primarily CD4+ T-cells and memory cells
- glandular neurodegeneration from apoptosis mediated by cytokines and inflammatory cells
- Associated conditions
- other autoimmune diseases
- primary biliary cholangitis
- CREST syndrome
- rheumatoid arthritis
- systemic lupus erythematosus
- marginal zone lymphoma
- viral infections
- hepatitis C virus
- EBV
- HIV
- other autoimmune diseases
- Prognosis
- patients are at risk for non-Hodgkin lymphoma and other autoimmune diseases
Presentation
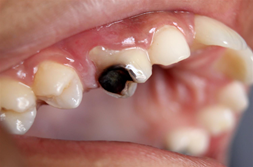
- Symptoms
- sicca symptoms in > 95% of patients
- ↓ saliva production causing dry mouth (xerostomia)
- ↓ tear production causing dry eyes (keratoconjunctivitis sicca or xerophthalmia)
- foreign body sensation
- dyspareunia in women
- constitutional symptoms
- fatigue
- weight loss
- sicca symptoms in > 95% of patients
- Physical exam
- cutaneous findings
- dry skin
- cheilitis
- ocular findings
- conjunctival injection
- oral findings
- dental caries or periodontal disease
- dry mucous membranes
- cutaneous findings
- bilateral parotid gland enlargement
Studies
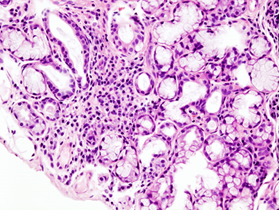
- Labs
- positive anti-SSB (anti-La) (50-70% of cases)
- positive antinuclear antibodies (50-90% of cases)
- possible positive rheumatoid factor (30-90% of cases)
- Corneal staining to assess ocular damage
- Labial salivary gland biopsy
- indication
- to confirm diagnosis, especially in patients with negative anti-Ro or anti-La antibodies
- findings
- dense inflammatory infiltrate in exocrine glands
- indication
- Making the diagnosis
- based on clinical presentation and laboratory studies
Differential
- Diabetes
- Hepatitis C
- Anticholinergic drug use
- Mumps
Treatment
- Medical
- artificial tears
- indication
- dry eyes
- indication
- pilocarpine or cevimeline
- indication
- dry eyes or dry mouth
- indication
- vitamin D supplementation
- indications
- for all patients
- indications
- artificial tears
- vitamin D deficiency may increase risk of neuropathy and lymphoma
Complications
- Dental caries
- Oral candidiasis
- Corneal abrasion or ulceration
- Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma
- Parotid gland infection


