Snapshot
- A 36-year-old female has been visiting her primary care physician very frequently over the past seven months because she is afraid she has an underlying illness. She has been experiencing mild, nonspecific abdominal pain off and on throughout this time. Despite reasssurances by her doctor, as well as a normal abdominal ultrasound and abdominal CT scan, she is still convinced something is being missed. Because of her fear, she has become socially withdrawn and spends much of her time at home researching diseases on the internet. (Illness anxiety disorder)
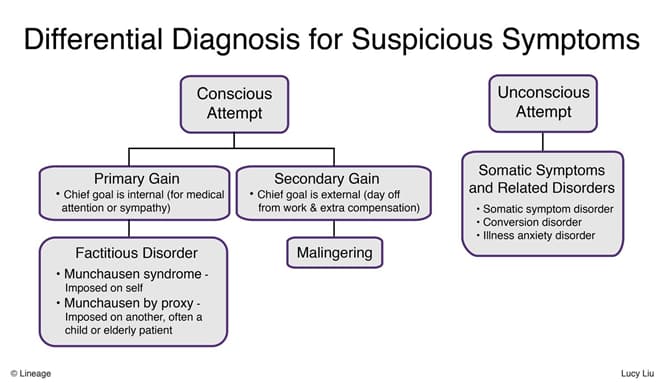
Somatic Symptom and Related Disorders
- Definition
- physical symptoms that cause mental distress
- in DSM-V, less of an emphasis on whether or not an underlying medical condition has been ruled out as a cause for the physical symptoms
- historically called “hysteria” or “somatization”
- Epidemiology
- F > M
- less educated
- lower socioecononimc status
- ethnic minorities
- Types
- somatic symptom disorder
- one or more physical symptoms that cause distress
- dysfunctional thoughts, feelings, or behaviors associated with the physical symptoms
- dysfunction is present for at least six months
- pain disorder
- chronic pain that causes significant distress or impairment
- psychological factors appear to influence the experience of the pain
- conversion disorder
- neurological impairment involving voluntary motor or sensory function with no primary neurological cause
- symptoms may include paralysis, blindness, mutism, or seizures
- cannot refer to sexual dysfunction or pain
- patient is aware of but indifferent toward symptoms, known as “la belle indifference”
- more common in adolescents and young adults
- neurological impairment involving voluntary motor or sensory function with no primary neurological cause
- illness anxiety disorder
- fear of having a serious illness
- mild or absent physical symptoms
- dysfunctional or maladaptive behaviors associated with health
- excessive check ups
- avoidance of certain behaviors associated with the potential illness
- preoccupation with illness despite medical evaluation and reassurance
- fear is present for at least six months
- factitious disorder
- deliberately faking or manufacturing symptoms in order to obtain sympathy from others and assume the sick role
- injuries
- infections
- hypogylycemia
- no external benefit, such as worker’s compensation, time off from work, etc.
- often involved with the healthcare industry in some way and has some degree of medical knowledge
- extreme subtype is “Munchausen syndrome”
- travels to numerous hospitals and clinics to seek treatment
- consents to highly invasive procedures
- M > F
- deliberately faking or manufacturing symptoms in order to obtain sympathy from others and assume the sick role
- malingering
- deliberately faking or exaggering symptoms for an external benefit, such as worker’s compensation, time off from work, avoidance of criminal prosecution etc.
- associated with antisocial personality disorder
- psychological factors affecting other medical conditions
- psychological distress or a maladaptive behavior that triggers, exacerbates, or prevents the treatment of a medical condition
- somatic symptom disorder


