Snapshot
- A 3-year-old girl presents to her pediatrician with a widespread rash. She recently had fevers and a sore throat. She has perioral fissues and a desquamating rash in the groin and neck. When light pressure is applied, the skin easily sloughs off. Superficial wound cultures and bacterial cultures are negative.
Introduction
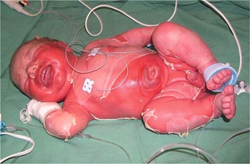
- Clinical definition
- Epidemiology
- incidence
- 9-25 per 100,000 children
- demographics
- affects neonates and children
- incidence
- Pathophysiology
- mechanism of injury
- Associated Staphylococcus aureus conditions
- children
- preceding respiratory tract infection
- preceding conjunctivitis
- preceding otitis media
- children
- Prognosis
- survival with treatment
- very good
Presentation
- Symptoms
- primary symptoms
- prodrome with irritability, malaise, fever, and sore throat
- primary symptoms
- Physical exam
- erythematous tender patches progressing to painful desquamation and superficial skin sloughing with “scalded” appearance
- generalized and flaccid bullae
- perioral and periorbital fissures
- mucous membranes not involved
- positive Nikolsky sign which describes a
- separation of epidermis from dermis with slight pressure
- distribution is often in the face, neck, groin, axillae, and other flexural surfaces
- mucosal surfaces not involved (vs. SJS & TEN)
Studies
- Labs
- blood cultures typically negative
- superficial wound cultures and bullae fluid cultures are sterile
- Biopsy
- indications
- if diagnosis of toxic epidermal necrolysis needs to be ruled out
- indications
- Histology
- intraepidermal cleavage
Differential
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
- full thickness epidermal cell necrosis and supepidermal cleavage
- Bullous impetigo
- honey-crusted erosions
- more widespread
- positive superficial wound cultures
Treatment
- Medical
- intravenous anti-staphylococcal antibiotics
- indications
- administered in the treatment of staphlococcal scalded skin syndrome
- modalities
- nafcillin or oxacillin in methicillin-sesitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA)
- indications
- intravenous anti-staphylococcal antibiotics
- vancomycin in cases of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
Complications
- Secondary infection of denuded skin


