- A 29-year-old woman at 36-weeks gestation presents to her obstetrician for a prenatal visit. She denies any bloody vaginal fluid production and endorses the presence of spontaneous fetal movement. Ultrasonography demonstrates infant size that is appropriate for gestational age. She undergoes a rectal and vaginal swab, which grows group B streptococci. Preparations are made to receive intrapartum penicillin G prophylaxis.
Introduction
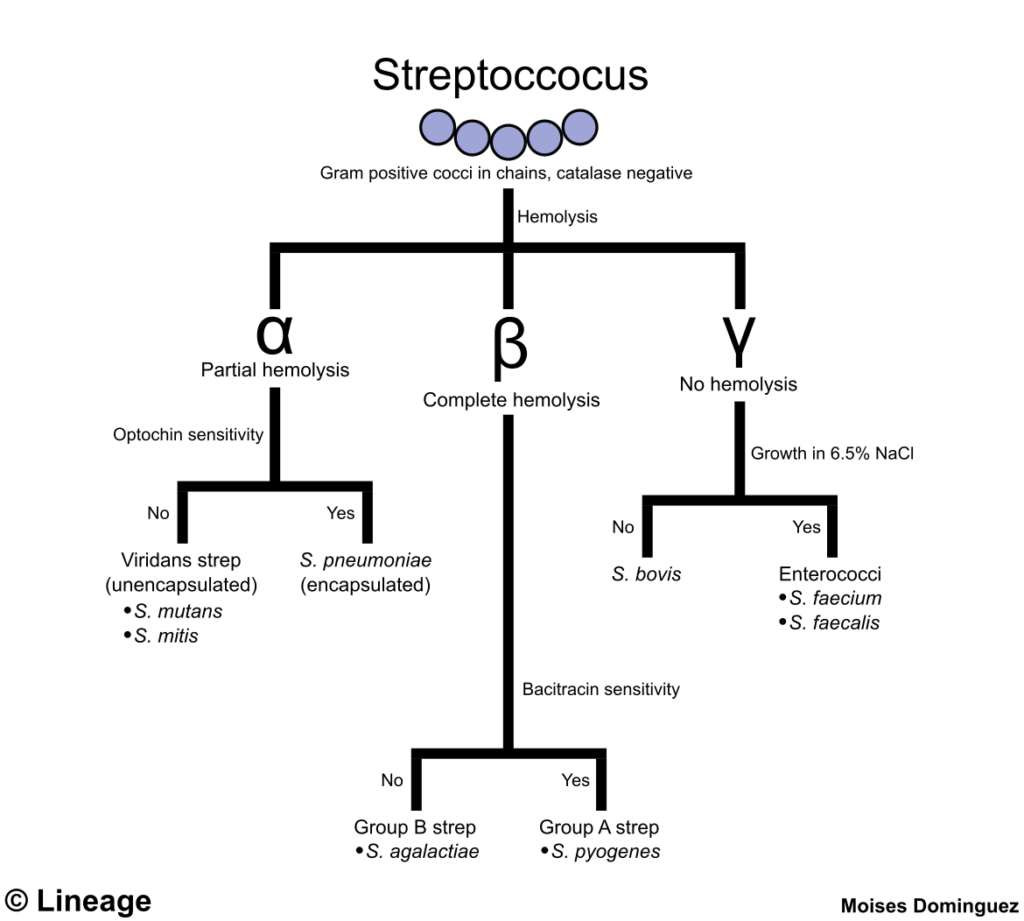
- Classification
- Reservoir
- vagina and gastrointestinal tract
- Prevention
- at 35-37 weeks gestation, a rectal and vaginal swab is performed to determine the presence of group B streptococcus (GBS)
- if the cultures return positive for GBS, patients receive intrapartum penicillin G or ampicillin prophylaxis
- at 35-37 weeks gestation, a rectal and vaginal swab is performed to determine the presence of group B streptococcus (GBS)
- Pathogenesis
- infection occurs in utero secondary to
- intraamniotic infection
- rupture of membranes
- passage through the vagina
- infection occurs in utero secondary to
- Associated conditions
- neonatal meningitis
- neonatal sepsis
- neonatal pneumonia
Presentation
- Symptoms/physical exam
- neonatal septicemia
- irritability
- lethargy
- respiratory distress (e.g., tachypnea, hypoxia, and grunting)
- neonatal meningitis
- irritability
- lethargy
- respiratory distress (e.g., tachypnea, hypoxia, and grunting)
- poor feeding and vomiting
- bulging fontanel
- nuchal rigidity
- neonatal pneumonia
- respiratory distress (e.g., tachypnea, hypoxia, and grunting)
- neonatal septicemia
- patients will have a diffuse alveolar pattern on chest radiography
Studies
- GBS isolation from a sterile body site (e.g., blood and cerebrospinal fluid)
Differential
- Neonatal meningitis by other organisms (e.g., E. coli and L. monocytogenes)
- differentiating factors
- E. coli
- gram-negative
- L. monocytogenes
- E. coli
- differentiating factors
- gram-positive rod
Treatment
- Medical
- penicillin G
- indication
- treatment of choice after GBS has been confirmed to be the only organism causing infection in the neonate and infant
- indication
- penicillin G



