Snapshot
- A 6-year-old boy presents to his pediatrician for sore throat and a headache. His symptoms began approximately 2 days ago and have not improved. The mother reports that the patient appears uncomfortable and feels warm. She says that he was born at 39-weeks gestation via a normal spontaneous vaginal delivery with no complications. He has received all of his vaccinations appropriate for his age. He has no significant past medical history and only takes a daily multivitamin. He has no allergies to medications known to the mother. Physical examination is notable for perioral crusted lesions with tonsilar swelling with exudates. A rapid antigen detection test is positive for Streptococcal pyogenes infection. He is started on oral penicillin.
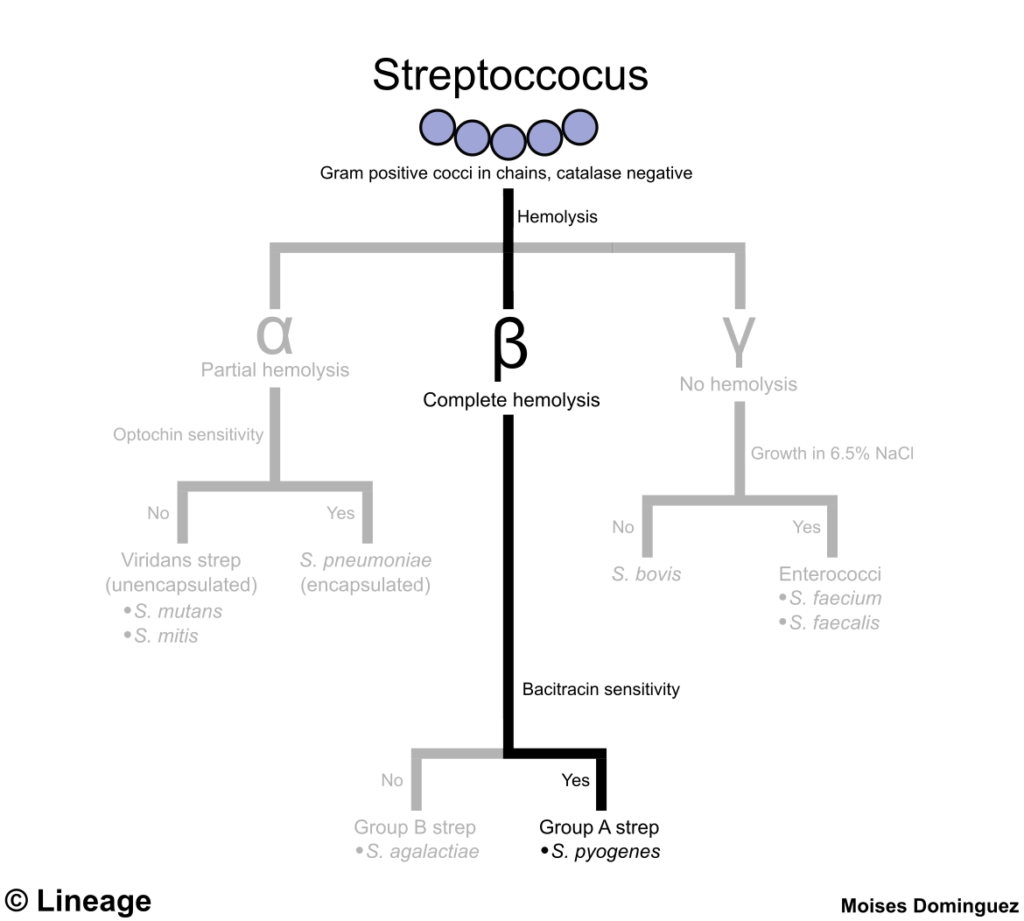
Introduction
- Classification
- gram-positive cocci
- Microbiology
- reservoir
- properties
- Lacefield group A
- bacitracin sensitive
- pyrrolidonyl arylamidase (PYR) positive
- hyaluronic acid capsule
- inhibits phagocytosis
- streptolysin O
- an oxygen labile enzyme that destroys both red and white blood cells, giving this organism its β-hemolytic property
- antibodies against streptolysin O (anti-ASO antibodies) allows checking ASO titers to determine if there was a recent Streptococcus pyogenes infection
- DNase B
- antibodies against DNase B (anti-DNase B) also indicate recent Streptococcus pyogenes infection
- pyogenic exotoxin (erythrogenic toxin)
- can result in scarlet fever
- can superstimulate T-cells, resulting in streptococcal toxic shock syndrome
- Associated conditions
- streptococcal pharyngitis
- streptococcal skin infections
- Scarlet fever
- delayed antibody-mediated reactions
- rheumatic fever
- poststreptococcal glomerulonephritis
Presentation



