Overview
Anatomy
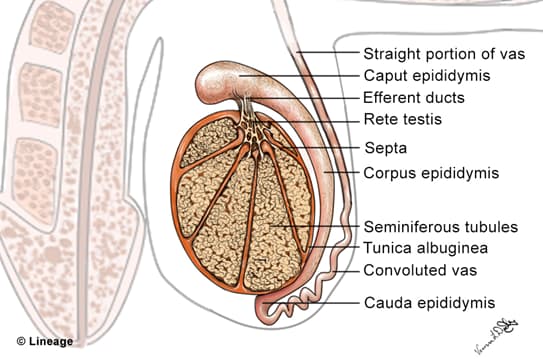
- Tunica albuginea
- an unusually thick, dense connective tissue capsule that covers each testis
- Lobules
- incomplete connective tissue septa that projects from tunica albuginea divides each testis into lobules
- Seminiferous tubules
- lobules consist of seminiferous tubules
- spermatogenesis occurs in seminiferous tubules
- seminiferous tubule epithelium contains spermatogenic cells and Sertoli cells
Spermatogenic Cells
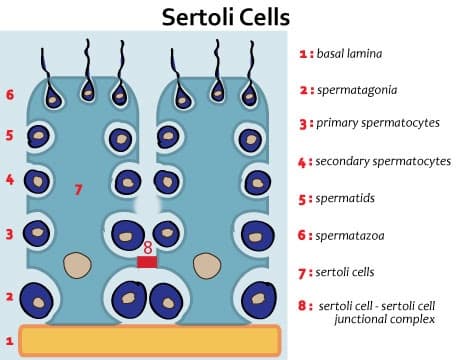
- Found within the seminiferous tubules
- Spermatogenic cells are organized in poorly defined layers of progressive development between adjacent Sertoli cells
- most immature spermatogenic cells, spermatogonia, rest on basal lamina
- most mature spermatogenic cells, spermatids, attach to apical portion of Sertoli cells and border lumen of seminiferous tubules
- dividing spermatogenic cells form daughter cells that remain joined by cytoplasmic bridges
Sertoli Cells
- Function to synthesize and secrete hormones including
- anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)
- released during embryogenesis and inhibits development of Müllerian (paramesonephric) ducts
- androgen-binding protein (ABP)
- released into luminal space of seminiferous tubules, near developing spermatogonia
- ABP binds testosterone and maintains high local testosterone levels, necessary for spermatogenesis
- inhibin
- provides negative-feedback on hypothalamic-pituitary axis and inhibits GnRH, LH, and FSH
- has more of an effect inhibiting FSH than GnRH or LH
- other products
- other products that support developing spermatogonia and support spermatogenesis
- anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)
- Sertoli cell junctional complexes
- extensive tight junctions bind adjacent Sertoli cells
- junctional complexes establish 2 epithelial compartments
- basal compartment
- occupies space between basal lamina and Sertoli cell – Sertoli cell junctional complexes
- contains spermatogonia
- luminal compartment
- occupies space above Sertoli cell – Sertoli cell junctional complexes
- contains primary spermatocytes, secondary spermatocytes, spermatids, and spermatozoa
- basal compartment
- blood-testis barrier
- established by junctional complexes
- spermatogenic cells differ antigenically from somatic cells;therefore, a blood-testis barrier is required to prevent spermatogenic cell exposure to immune system and a resulting autoimmune response



