Snapshot
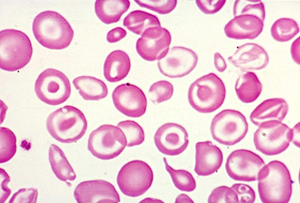
- A 22-year-old Vietnamese woman presents for a routine gyn exam. Her menstrual cycle is normal, and there is no evidence of other bleeding. Guaiac is negative. Her hemoglobin is at 11 (12-16), RBC is 5.8 (3.5-5.5), and an MCV of 70 (80-100) with a normal RDW of 10. WBC and platelets are normal. Hemoglobin electrophoresis shows an increase in the amount of Hgb A2, and Hgb F.
Introduction
- Autosomal recessive disease caused by decreased production of hemoglobin
- may involve mutations in α (α-thalassemia) or β (β-thalassemia) globin gene
- There are 4 α genes (2 on each chromosome) and 2 β genes that make up three forms of Hgb
- Hgb A
- subunits: α,α,β,β
- 96-98% of adult hemoglobin
- Hgb A2
- subunits: α,α,δ,δ
- present in trace amounts in adults.
- Hgb F
- subunits: α,α,γ,γ
- declines in the first year of life
- cannot bind 2,3 DPG so has a left-shifted curve
- Hgb A
- α-thalassemia types
- 1 gene deletion is asymptomatic
- 2 gene deletion is associated with a mild anemia with RBC hyperplasia
- called α-thalassemia trait
- seen in Asians and Africans
- Asians more commonly have a deletion of two α genes on 1 chromosome (cis deletion)
- Africans more commonly have a deletion of 1 α gene from each chromosome (trans deletion)
- 3 gene deletion is associated with severe anemia
- 4 gene deletion is not compatible with life
- will cause hydrops fetalis
- β-thalassemia types
- 1 gene involvement
- chain may be truncated (β+) or deleted (β0)
- β/β+ is the most benign form
- may be caused by mutation in Kozak consensus sequence
- 1 gene involvement
- α,α,α,α hemoglobin present
Presentation
- Symptoms
- α-thalassemia
- mild anemia in 2 gene deletion
- severe anemia in 3 gene deletion
- symptoms being at birth
- α-thalassemia
- Physical exam
- β-thalassemia
- major form
- β-thalassemia
- hepatosplenomegaly due to chronic hemolysis, additionally exacerbated by extramedullary hematopoiesis in these organs
Evaluation
- Peripheral smear
- 3 gene deletion α-thalassemia
- target, hypochromic, microcytic cells, with Heinz bodies from HbH
- β-thalassemia minor
- target, hypochromic, microcytic cells
- β-thalassemia major
- nucleated RBCs
- target, hypochromic, microcytic cells
- 3 gene deletion α-thalassemia
- Hemoglobin gel-electrophoresis
- α-thalassemia trait
- normal
- 3 gene deletion α-thalassemia
- HbH (β,β,β,β)
- 4 gene deletion α-thalassemia
- Hb Barts (γ,γ,γ,γ)
- β-thalassemia major
- ↑ HbA2, HbF
- no HbA
- α-thalassemia trait
- Imaging
- β-thalassemia major
- hair-on-end/crew cut appearance of the skull
- β-thalassemia major
- secondary to extramedullary hematopoiesis in the skull
Treatment
Prognosis, Prevention, and Complications
- β-thalassemia major
- ↑ risk of B19-mediated aplastic crises
- Thalassemia trait
- protects against malaria


